Sometimes you can meet a case when a cyber-attacker uses VPN to establish a reliable channel between C2 server and infected IT-infrastructure. And, as Threat Intelligence experts say, attackers often use native Windows VPN connection tools and Windows .pbk (phonebook) files. Lets find out how we can detect it using a memory dump.
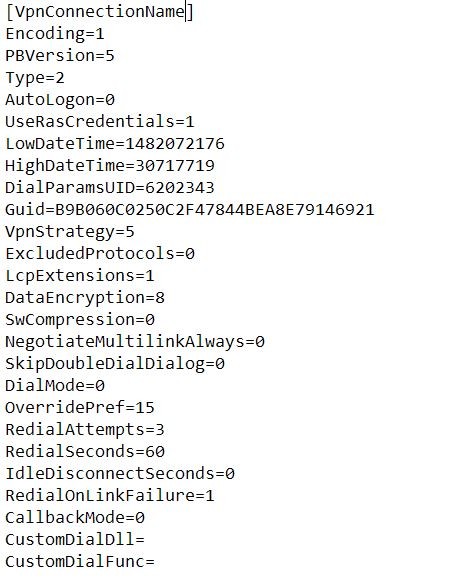
What is .pbk file and how does it look inside? It's just a text file with a lot of different parameters using when VPN connection is establishing.
The phonebook file can be executed with doubleclick or via cmd/bat script (or from the command console of course). But there are two different tools are using for the first and the second way: rasdial and rasphone. Therefore we can use two different ways in a digital forensics process. At the start of both ways we should use a volatility tool to get and check a process list:
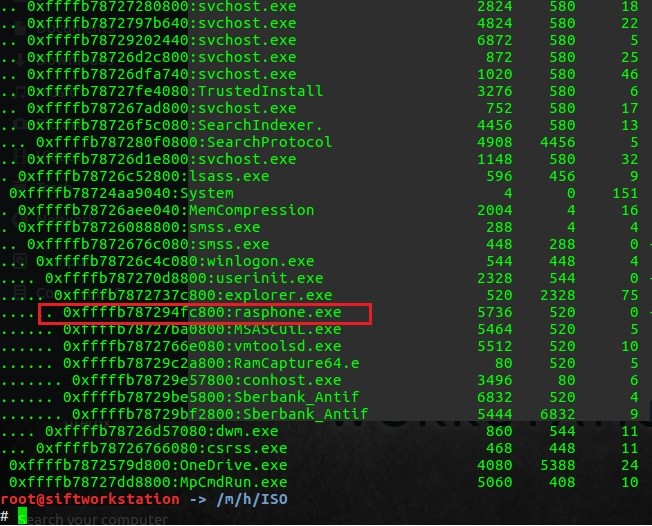
If a rasphone process being detected, it's possible a trace of using phonebook with doubleclick from RDP session for example. What useful information can we also find here? Let's open this dump file in FTK Imager and try to look for any .pbk parameters. I used a «PhoneNumber=» for this case.
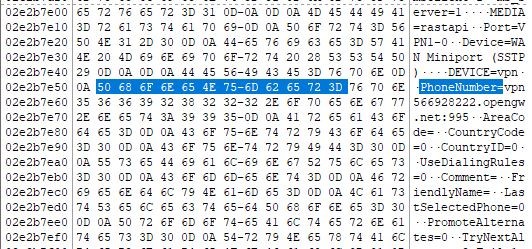
Here you see a remote address for this VPN connection and a port number. vpn566928222.opengw.net:995 From this point we can detect a current connection's service name in RAM, using a port number and volatility netscan command.
![]()
If the dumped system is still alive you can kill this process or you can continue research. Of course you should know more about remote IP address:
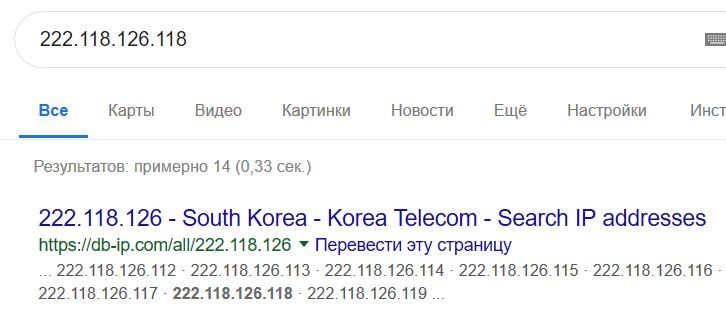
It seems likle a free anonymous VPN server and there are a lot of them in the Internet. And this is a question — what application uses this VPN connection on the infected station?
I know that VPN is a connection to another private network and my workstation has got another IP address in foreign subnet. My local subnet is 192.168.145.0/24 but there are several services with different local IP adresses (10.211.1.0/24) in results of volatility netscan.
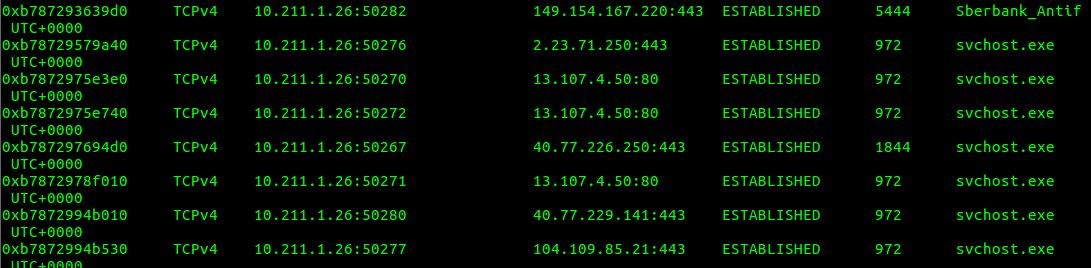
Several destination IPs are for Microsoft cervices and one suspicious service Sberbank_Antifraud connected to 149.154.167.220 — it's a Telegram Messenger pool IP So, now you can start to investigate how this process appeared on this machine.
Ok, another way is about cmd/bat-driven VPN connection with .pbk files.
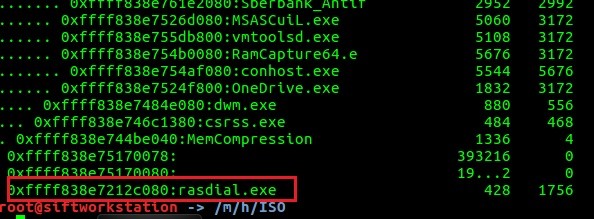
Unlike rasphone, rasdial process is a marker for command line- or script-driven VPN connection. Let's check rasdial syntax here ss64.com/nt/rasdial.html and try to find /PHONEBOOK: parameter in memory dump using FTK Imager:
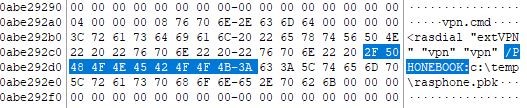
Voila! We've found a full path to the phonebook file (so, if it's deleted you can try to carve it), the name of a .cmd script and login/password («vpn», «vpn») for «extVPN» connection!
Further steps are the same as for rasphone way: looking for a «PhoneNumber=» parameter, finding a VPN session and a suspicious service with foreing local IP address.
Thank you again for attention! I'll be back soon with a new good stuff!
Автор: volnodumcev