Пожалуй, самой закрытой технологией в пользовательском сегменте является сотовая связь. Очень немногие знают о том, как на самом деле работают телефоны и модемы, отчего им часто приписывают всякие мифические свойства. Как насчёт попробовать запустить полностью открытую реализацию модема стандарта 4G? Именно этим я и предлагаю заняться.

Итак, в сегодняшней статье поговорим о том, как взаимодействовать с мобильной сетью при помощи SDR. Попутно узнаем, какой софт для этого существует, и соберём самый дорогой 4G-модем в истории.
Традиционно будет много интересного.
❯ Суть такова
В начале года я рассматривал запуск домашней сети 4G на базе софта srsRAN и подключал к ней обычные телефоны. Сегодня мы посмотрим на эту задачу с противоположной стороны — создадим устройство, которое будет видеть сеть оператора и получать от неё данные. А заодно и подключим компьютер к мобильному интернету без использования заводского телефона или модема.
❯ Что за софт мы будем использовать?
Как я уже говорил, открытая реализация 4G не одна. Но по части «пользовательских» устройств всё несколько беднее — есть софт GR-LTE (который, правда, служит для декодирования сигналов LTE, а не для работы с сетью), а также srsUE от всё того же Software Radio Systems (srsRAN). Последний нам и нужен: это полноценная софтовая реализация LTE-модема. Изначально это ПО предназначалось для совместной работы с srsENB, то есть предполагалось, что у вас есть два ПК, на одном из которых запущена БС (eNodeB), а на другом — абонентское устройство (User Equipment). Такая связка позволяет анализировать всю работу сети полностью. Но второго SDR у меня нет, так что поговорим о самом интересном: как подключиться при помощи этого софта к обычной сети и, на этот раз, раздать интернет на компьютер.
Если у вас нет SDR, то можно воспользоваться эмулятором БС, который также описан на сайте srsRAN.
Внимание!
В данной статье описывается взаимодействие с коммерческими сотовыми сетями. Правильно настроенный софт никак не мешает их работе, но вы в любом случае должны иметь представление о том, что собираетесь сделать.
❯ Что нужно, чтобы запустить эмулятор модема?
Самое время определиться с оборудованием. Итак, для проведения опытов понадобится примерно следующий набор:
- Компьютер с Linux. Как и в прошлых опытах, машина должна быть достаточно мощной, чтобы обрабатывать данные с SDR. Также обязателен порт USB 3.0.
- SDR. Именно из-за него статья имеет класс «Сложный», так как подобные устройства весьма дороги и есть не у всех. Подойдут всё те же модели, что годятся для eNodeB: USRP, BladeRF или любой другой, совместимый с драйвером SoapySDR. Также srsRAN можно пересобрать под LimeSDR, но ввиду того, что такого девайса у меня нет, я не интересовался, как это сделать.
- Антенны для SDR. В идеале — те, которые специально рассчитаны на использование в сетях 3G/4G.
- Симка. Лучше, если их будет несколько, разных операторов, так как с какими-то работает стабильно, а с какими-то — не очень. Само собой, карта должна быть живая и с ненулевым балансом.
- Считыватель смарт-карт. Обязательно совместимый со стандартом PC/SC, иначе работать не будет. Всякие китайские «SIM card reader» с проприетарным софтом не подойдут.
- Телефон. Непосредственно в запуске он участия принимать не будет, но для подготовки понадобится.
GPS-DO или другой подобный источник стабильной частоты, в отличие от БС, использовать необязательно.
❯ Обзор оборудования
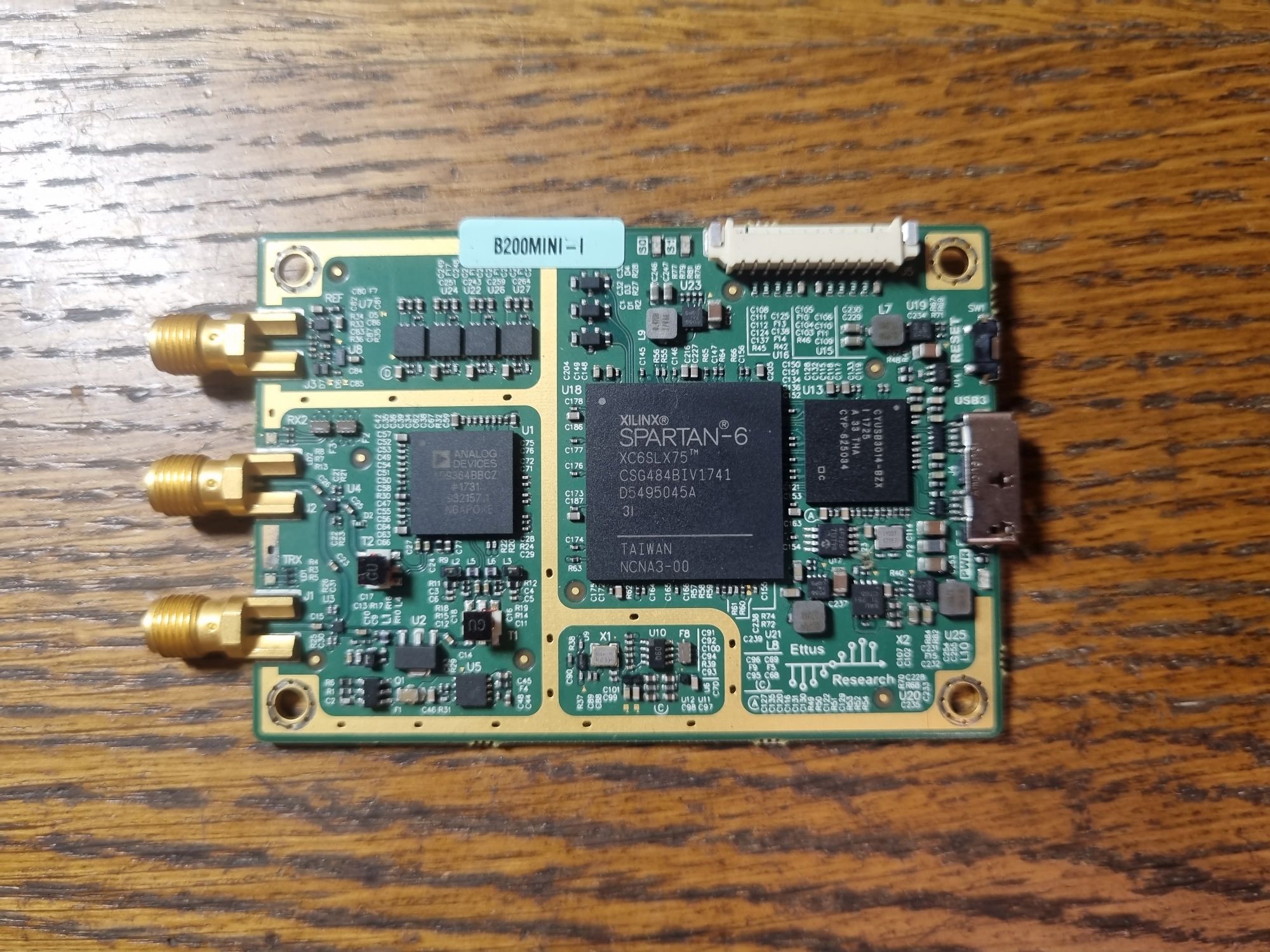

Перво-наперво идёт, конечно, сам SDR — USRP B200mini-i и комплект антенн к нему.

Считыватель.


Такой экземпляр можно встретить в любом месте, где есть какие-то СКЗИ или авторизация по смарт-карте, то есть практически повсеместно. Если под рукой такого нет, его можно легко купить, благо стоит он всего-ничего.


А вот пример тех, которые не подойдут — пин-пады со считывателями карт, а также проприетарные девайсы.
В общем-то, больше ничего примечательного сегодня не потребуется.
❯ Ставим софт
По умолчанию srsUE не поддерживает работу со считывателем смарт-карт, поэтому его необходимо пересобрать из исходников. Именно этим мы сейчас и займёмся.
Для начала устанавливаем зависимости:
sudo apt-get install build-essential cmake libfftw3-dev libmbedtls-dev libboost-program-options-dev libconfig++-dev libsctp-dev
sudo apt-get install libpcsclite-dev pcscd pcsc-toolsДля запуска я рекомендую использовать дистрибутив DragonOS. Там уже установлены все необходимые зависимости. В случае использования именно его первую строчку надо пропустить. Второй строчкой устанавливаем библиотеки и софт для работы со смарт-картами.
Теперь клонируем и собираем:
git clone https://github.com/srsRAN/srsRAN_4G.git
cd srsRAN_4G
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../
make
sudo make install
srsran_install_configs.sh user
Если у вас уже есть какие-то файлы конфигурации (в частности, по пути /etc/srsran), то перед началом опытов их надо снести. Как обычно, на случай, если у вас вдруг возникнут проблемы при компиляции, ссылку на уже готовый софт я оставлю тут.
Теперь подключаем к компьютеру SDR и делаем тестовый запуск:
cd srsue/src
sudo ./srsue
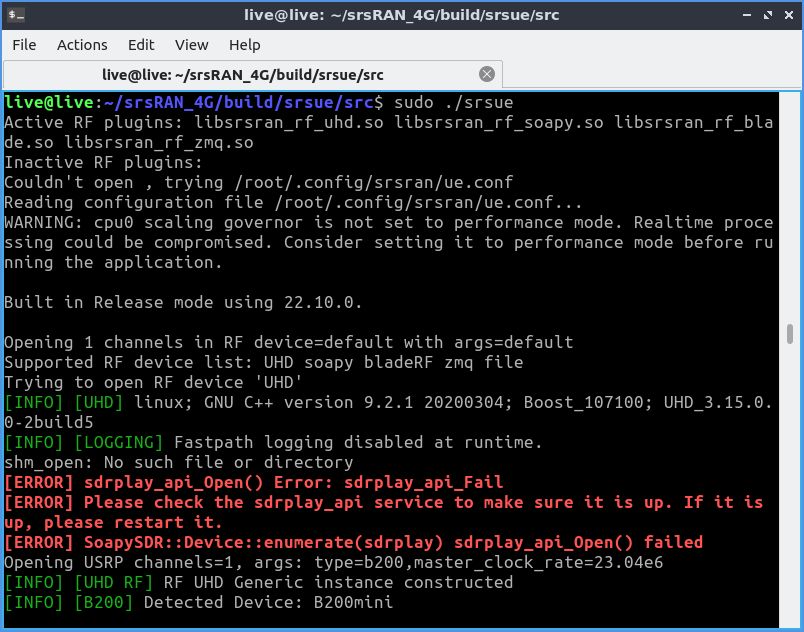
Если после этого софт не вылетел, а в консоли появилось «Attaching UE...», значит, мы на правильном пути.
❯ Конфигурация
На сайте srsRAN всё описывается просто — запустить ПО с единственным параметром, и в путь. На деле этого недостаточно: если в srsEPC имеются некоторые допущения, то коммерческая сеть ошибок не прощает и криво сконфигурированный UE принимать не будет. Так что перед тем, как приступить к «боевому» запуску, нужно настроить параметры конфигурации. Лежат они по пути /root/.config/srsran/ue.conf.
Открываем этот файл и приводим его к следующему виду:
#####################################################################
# srsUE configuration file
#####################################################################
#####################################################################
# RF configuration
#
# freq_offset: Uplink and Downlink optional frequency offset (in Hz)
# tx_gain: Transmit gain (dB).
# rx_gain: Optional receive gain (dB). If disabled, AGC if enabled
# srate: Optional fixed sampling rate (Hz), corresponding to cell bandwidth. Must be set for 5G-SA.
#
# nof_antennas: Number of antennas per carrier (all carriers have the same number of antennas)
# device_name: Device driver family. Supported options: "auto" (uses first found), "UHD" or "bladeRF"
# device_args: Arguments for the device driver. Options are "auto" or any string.
# Default for UHD: "recv_frame_size=9232,send_frame_size=9232"
# Default for bladeRF: ""
# device_args_2: Arguments for the RF device driver 2.
# device_args_3: Arguments for the RF device driver 3.
# time_adv_nsamples: Transmission time advance (in number of samples) to compensate for RF delay
# from antenna to timestamp insertion.
# Default "auto". B210 USRP: 100 samples, bladeRF: 27.
# continuous_tx: Transmit samples continuously to the radio or on bursts (auto/yes/no).
# Default is auto (yes for UHD, no for rest)
#####################################################################
[rf]
freq_offset = 0
tx_gain = 80
rx_gain = 40
srate = 23.04e6
#nof_antennas = 1
# For best performance in 2x2 MIMO and >= 15 MHz use the following device_args settings:
# USRP B210: num_recv_frames=64,num_send_frames=64
# For best performance when BW<5 MHz (25 PRB), use the following device_args settings:
# USRP B210: send_frame_size=512,recv_frame_size=512
#device_args = auto
#time_adv_nsamples = auto
#continuous_tx = auto
# Example for ZMQ-based operation with TCP transport for I/Q samples
#device_name = zmq
#device_args = tx_port=tcp://*:2001,rx_port=tcp://localhost:2000,id=ue,base_srate=23.04e6
#####################################################################
# EUTRA RAT configuration
#
# dl_earfcn: Downlink EARFCN list.
#
# Optional parameters:
# dl_freq: Override DL frequency corresponding to dl_earfcn
# ul_freq: Override UL frequency corresponding to dl_earfcn
# nof_carriers: Number of carriers
#####################################################################
[rat.eutra]
dl_earfcn = 3250
#nof_carriers = 1
#####################################################################
# NR RAT configuration
#
# Optional parameters:
# bands: List of support NR bands seperated by a comma (default 78)
# nof_carriers: Number of NR carriers (must be at least 1 for NR support)
#####################################################################
[rat.nr]
# bands = 78
# nof_carriers = 0
#####################################################################
# Packet capture configuration
#
# Packet capture is supported at the MAC, MAC_NR, and NAS layer.
# MAC-layer packets are captured to file a the compact format decoded
# by the Wireshark. For decoding, use the UDP dissector and the UDP
# heuristic dissection. Edit the preferences (Edit > Preferences >
# Protocols > DLT_USER) for DLT_USER to add an entry for DLT=149 with
# Protocol=udp. Further, enable the heuristic dissection in UDP under:
# Analyze > Enabled Protocols > MAC-LTE > mac_lte_udp and MAC-NR > mac_nr_udp
# For more information see: https://wiki.wireshark.org/MAC-LTE
# Using the same filename for mac_filename and mac_nr_filename writes both
# MAC-LTE and MAC-NR to the same file allowing a better analysis.
# NAS-layer packets are dissected with DLT=148, and Protocol = nas-eps.
#
# enable: Enable packet captures of layers (mac/mac_nr/nas/none) multiple option list
# mac_filename: File path to use for MAC packet capture
# mac_nr_filename: File path to use for MAC NR packet capture
# nas_filename: File path to use for NAS packet capture
#####################################################################
[pcap]
enable = none
mac_filename = /tmp/ue_mac.pcap
mac_nr_filename = /tmp/ue_mac_nr.pcap
nas_filename = /tmp/ue_nas.pcap
#####################################################################
# Log configuration
#
# Log levels can be set for individual layers. "all_level" sets log
# level for all layers unless otherwise configured.
# Format: e.g. phy_level = info
#
# In the same way, packet hex dumps can be limited for each level.
# "all_hex_limit" sets the hex limit for all layers unless otherwise
# configured.
# Format: e.g. phy_hex_limit = 32
#
# Logging layers: rf, phy, mac, rlc, pdcp, rrc, nas, gw, usim, stack, all
# Logging levels: debug, info, warning, error, none
#
# filename: File path to use for log output. Can be set to stdout
# to print logs to standard output
# file_max_size: Maximum file size (in kilobytes). When passed, multiple files are created.
# If set to negative, a single log file will be created.
#####################################################################
[log]
all_level = warning
phy_lib_level = none
all_hex_limit = 32
filename = /tmp/ue.log
file_max_size = -1
#####################################################################
# USIM configuration
#
# mode: USIM mode (soft/pcsc)
# algo: Authentication algorithm (xor/milenage)
# op/opc: 128-bit Operator Variant Algorithm Configuration Field (hex)
# - Specify either op or opc (only used in milenage)
# k: 128-bit subscriber key (hex)
# imsi: 15 digit International Mobile Subscriber Identity
# imei: 15 digit International Mobile Station Equipment Identity
# pin: PIN in case real SIM card is used
# reader: Specify card reader by it's name as listed by 'pcsc_scan'. If empty, try all available readers.
#####################################################################
[usim]
mode = pcsc
#reader =
pin = 0000
imei = 352406718839858
#####################################################################
# RRC configuration
#
# ue_category: Sets UE category (range 1-5). Default: 4
# release: UE Release (8 to 15)
# feature_group: Hex value of the featureGroupIndicators field in the
# UECapabilityInformation message. Default 0xe6041000
# mbms_service_id: MBMS service id for autostarting MBMS reception
# (default -1 means disabled)
# mbms_service_port: Port of the MBMS service
# nr_measurement_pci: NR PCI for the simulated NR measurement. Default: 500
# nr_short_sn_support: Announce PDCP short SN support. Default: true
#####################################################################
[rrc]
ue_category = 1
#release = 8
#feature_group = 0xe6041000
#mbms_service_id = -1
#mbms_service_port = 4321
#####################################################################
# NAS configuration
#
# apn: Set Access Point Name (APN)
# apn_protocol: Set APN protocol (IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4v6.)
# user: Username for CHAP authentication
# pass: Password for CHAP authentication
# force_imsi_attach: Whether to always perform an IMSI attach
# eia: List of integrity algorithms included in UE capabilities
# Supported: 1 - Snow3G, 2 - AES, 3 - ZUC
# eea: List of ciphering algorithms included in UE capabilities
# Supported: 0 - NULL, 1 - Snow3G, 2 - AES, 3 - ZUC
#####################################################################
[nas]
apn = internet.mts.ru
apn_protocol = ipv4
user = mts
pass = mts
#force_imsi_attach = false
#eia = 1,2,3
#eea = 0,1,2,3
#####################################################################
# Slice configuration
#
# enable: Enable a specific slice
# nssai-sst: Specfic Slice Type
# nssai-sd: Slice diffentiator
#####################################################################
[slicing]
#enable = false
#nssai-sst = 1
#nssai-sd = 1
#####################################################################
# GW configuration
#
# netns: Network namespace to create TUN device. Default: empty
# ip_devname: Name of the tun_srsue device. Default: tun_srsue
# ip_netmask: Netmask of the tun_srsue device. Default: 255.255.255.0
#####################################################################
[gw]
#netns =
#ip_devname = tun_srsue
#ip_netmask = 255.255.255.0
#####################################################################
# GUI configuration
#
# Simple GUI displaying PDSCH constellation and channel freq response.
# (Requires building with srsGUI)
# enable: Enable the graphical interface (true/false)
#####################################################################
[gui]
enable = false
#####################################################################
# Channel emulator options:
# enable: Enable/Disable internal Downlink/Uplink channel emulator
#
# -- AWGN Generator
# awgn.enable: Enable/disable AWGN generator
# awgn.snr: SNR in dB
# awgn.signal_power: Received signal power in decibels full scale (dBfs)
#
# -- Fading emulator
# fading.enable: Enable/disable fading simulator
# fading.model: Fading model + maximum doppler (E.g. none, epa5, eva70, etu300, etc)
#
# -- Delay Emulator delay(t) = delay_min + (delay_max - delay_min) * (1 + sin(2pi*t/period)) / 2
# Maximum speed [m/s]: (delay_max - delay_min) * pi * 300 / period
# delay.enable: Enable/disable delay simulator
# delay.period_s: Delay period in seconds.
# delay.init_time_s: Delay initial time in seconds.
# delay.maximum_us: Maximum delay in microseconds
# delay.minumum_us: Minimum delay in microseconds
#
# -- Radio-Link Failure (RLF) Emulator
# rlf.enable: Enable/disable RLF simulator
# rlf.t_on_ms: Time for On state of the channel (ms)
# rlf.t_off_ms: Time for Off state of the channel (ms)
#
# -- High Speed Train Doppler model simulator
# hst.enable: Enable/Disable HST simulator
# hst.period_s: HST simulation period in seconds
# hst.fd_hz: Doppler frequency in Hz
# hst.init_time_s: Initial time in seconds
#####################################################################
[channel.dl]
#enable = false
[channel.dl.awgn]
#enable = false
#snr = 30
[channel.dl.fading]
#enable = false
#model = none
[channel.dl.delay]
#enable = false
#period_s = 3600
#init_time_s = 0
#maximum_us = 100
#minimum_us = 10
[channel.dl.rlf]
#enable = false
#t_on_ms = 10000
#t_off_ms = 2000
[channel.dl.hst]
#enable = false
#period_s = 7.2
#fd_hz = 750.0
#init_time_s = 0.0
[channel.ul]
#enable = false
[channel.ul.awgn]
#enable = false
#n0 = -30
[channel.ul.fading]
#enable = false
#model = none
[channel.ul.delay]
#enable = false
#period_s = 3600
#init_time_s = 0
#maximum_us = 100
#minimum_us = 10
[channel.ul.rlf]
#enable = false
#t_on_ms = 10000
#t_off_ms = 2000
[channel.ul.hst]
#enable = false
#period_s = 7.2
#fd_hz = -750.0
#init_time_s = 0.0
#####################################################################
# PHY configuration options
#
# rx_gain_offset: RX Gain offset to add to rx_gain to calibrate RSRP readings
# prach_gain: PRACH gain (dB). If defined, forces a gain for the tranmsission of PRACH only.,
# Default is to use tx_gain in [rf] section.
# cqi_max: Upper bound on the maximum CQI to be reported. Default 15.
# cqi_fixed: Fixes the reported CQI to a constant value. Default disabled.
# snr_ema_coeff: Sets the SNR exponential moving average coefficient (Default 0.1)
# snr_estim_alg: Sets the noise estimation algorithm. (Default refs)
# Options: pss: use difference between received and known pss signal,
# refs: use difference between noise references and noiseless (after filtering)
# empty: use empty subcarriers in the boarder of pss/sss signal
# pdsch_max_its: Maximum number of turbo decoder iterations (Default 4)
# pdsch_meas_evm: Measure PDSCH EVM, increases CPU load (default false)
# nof_phy_threads: Selects the number of PHY threads (maximum 4, minimum 1, default 3)
# equalizer_mode: Selects equalizer mode. Valid modes are: "mmse", "zf" or any
# non-negative real number to indicate a regularized zf coefficient.
# Default is MMSE.
# correct_sync_error: Channel estimator measures and pre-compensates time synchronization error. Increases CPU usage,
# improves PDSCH decoding in high SFO and high speed UE scenarios.
# sfo_ema: EMA coefficient to average sample offsets used to compute SFO
# sfo_correct_period: Period in ms to correct sample time to adjust for SFO
# sss_algorithm: Selects the SSS estimation algorithm. Can choose between
# {full, partial, diff}.
# estimator_fil_auto: The channel estimator smooths the channel estimate with an adaptative filter.
# estimator_fil_stddev: Sets the channel estimator smooth gaussian filter standard deviation.
# estimator_fil_order: Sets the channel estimator smooth gaussian filter order (even values perform better).
# The taps are [w, 1-2w, w]
#
# snr_to_cqi_offset: Sets an offset in the SNR to CQI table. This is used to adjust the reported CQI.
#
# interpolate_subframe_enabled: Interpolates in the time domain the channel estimates within 1 subframe. Default is to average.
#
# pdsch_csi_enabled: Stores the Channel State Information and uses it for weightening the softbits. It is only
# used in TM1. It is True by default.
#
# pdsch_8bit_decoder: Use 8-bit for LLR representation and turbo decoder trellis computation (Experimental)
# force_ul_amplitude: Forces the peak amplitude in the PUCCH, PUSCH and SRS (set 0.0 to 1.0, set to 0 or negative for disabling)
#
# in_sync_rsrp_dbm_th: RSRP threshold (in dBm) above which the UE considers to be in-sync
# in_sync_snr_db_th: SNR threshold (in dB) above which the UE considers to be in-sync
# nof_in_sync_events: Number of PHY in-sync events before sending an in-sync event to RRC
# nof_out_of_sync_events: Number of PHY out-sync events before sending an out-sync event to RRC
#
# force_N_id_2: Force using a specific PSS (set to -1 to allow all PSSs).
# force_N_id_1: Force using a specific SSS (set to -1 to allow all SSSs).
#
#####################################################################
[phy]
#rx_gain_offset = 62
#prach_gain = 30
#cqi_max = 15
#cqi_fixed = 10
#snr_ema_coeff = 0.1
#snr_estim_alg = refs
#pdsch_max_its = 8 # These are half iterations
#pdsch_meas_evm = false
#nof_phy_threads = 3
#equalizer_mode = mmse
#correct_sync_error = false
#sfo_ema = 0.1
#sfo_correct_period = 10
#sss_algorithm = full
#estimator_fil_auto = false
#estimator_fil_stddev = 1.0
#estimator_fil_order = 4
#snr_to_cqi_offset = 0.0
#interpolate_subframe_enabled = false
#pdsch_csi_enabled = true
#pdsch_8bit_decoder = false
#force_ul_amplitude = 0
#detect_cp = false
#in_sync_rsrp_dbm_th = -130.0
#in_sync_snr_db_th = 3.0
#nof_in_sync_events = 10
#nof_out_of_sync_events = 20
#force_N_id_2 = 1
#force_N_id_1 = 10
#####################################################################
# PHY NR specific configuration options
#
# store_pdsch_ko: Dumps the PDSCH baseband samples into a file on KO reception
#
#####################################################################
[phy.nr]
#store_pdsch_ko = false
#####################################################################
# CFR configuration options
#
# The CFR module provides crest factor reduction for the transmitted signal.
#
# enable: Enable or disable the CFR. Default: disabled
#
# mode: manual: CFR threshold is set by cfr_manual_thres (default).
# auto_ema: CFR threshold is adaptive based on the signal PAPR. Power avg. with Exponential Moving Average.
# The time constant of the averaging can be tweaked with the ema_alpha parameter.
# auto_cma: CFR threshold is adaptive based on the signal PAPR. Power avg. with Cumulative Moving Average.
# Use with care, as CMA's increasingly slow response may be unsuitable for most use cases.
#
# strength: Ratio between amplitude-limited vs unprocessed signal (0 to 1). Default: 1
# manual_thres: Fixed manual clipping threshold for CFR manual mode. Default: 2
# auto_target_papr: Signal PAPR target (in dB) in CFR auto modes. output PAPR can be higher due to peak smoothing. Default: 7
# ema_alpha: Alpha coefficient for the power average in auto_ema mode. Default: 1/7
#
#####################################################################
[cfr]
#enable = false
#mode = manual
#manual_thres = 2.0
#strength = 1.0
#auto_target_papr = 7.0
#ema_alpha = 0.0143
#####################################################################
# Simulation configuration options
#
# The UE simulation supports turning on and off airplane mode in the UE.
# The actions are carried periodically until the UE is stopped.
#
# airplane_t_on_ms: Time to leave airplane mode turned on (in ms)
#
# airplane_t_off_ms: Time to leave airplane mode turned off (in ms)
#
#####################################################################
[sim]
#airplane_t_on_ms = -1
#airplane_t_off_ms = -1
#####################################################################
# General configuration options
#
# metrics_csv_enable: Write UE metrics to CSV file.
#
# metrics_period_secs: Sets the period at which metrics are requested from the UE.
#
# metrics_csv_filename: File path to use for CSV metrics.
#
# tracing_enable: Write source code tracing information to a file.
#
# tracing_filename: File path to use for tracing information.
#
# tracing_buffcapacity: Maximum capacity in bytes the tracing framework can store.
#
# have_tti_time_stats: Calculate TTI execution statistics using system clock
#
# metrics_json_enable: Write UE metrics to JSON file.
#
# metrics_json_filename: File path to use for JSON metrics.
#
#####################################################################
[general]
#metrics_csv_enable = false
#metrics_period_secs = 1
#metrics_csv_filename = /tmp/ue_metrics.csv
#have_tti_time_stats = true
#tracing_enable = true
#tracing_filename = /tmp/ue_tracing.log
#tracing_buffcapacity = 1000000
#metrics_json_enable = false
#metrics_json_filename = /tmp/ue_metrics.json
Разберёмся с параметрами, которые нужно изменить.
- srate — частота дискретизации SDR. Ставим максимальную поддерживаемую для вашего устройства.
- dl_earfcn — номер канала, на котором UE будет искать вышку.
- mode — тип SIM-карты (soft — виртуальная, pcsc — настоящая). Устанавливаем pcsc.
- reader — считыватель. Если значение пусто, то будут проверены все имеющиеся.
- pin — PIN симки.
- imei — IMEI, которым будет представляться UE.
- apn — APN вашей точки доступа.
- login — логин.
- pass — пароль.
srsUE не проходится по всем доступным ему каналам, как это делает телефон. Поэтому для работы необходимо указать EARFCN, на котором работает вышка оператора.
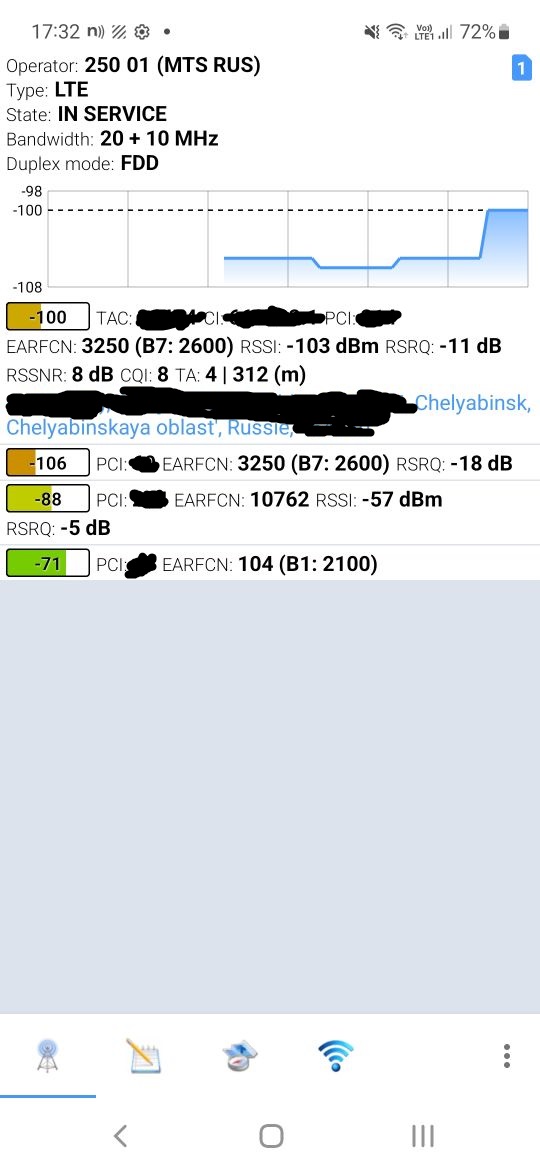
На телефоне открываем Net Monitor и запоминаем номер канала от БС с хорошим сигналом, после чего заносим его в качестве значения параметра. Также надо отрубить запрос ПИНа у симки, либо указать ПИН в соответствующем поле в конфиге.
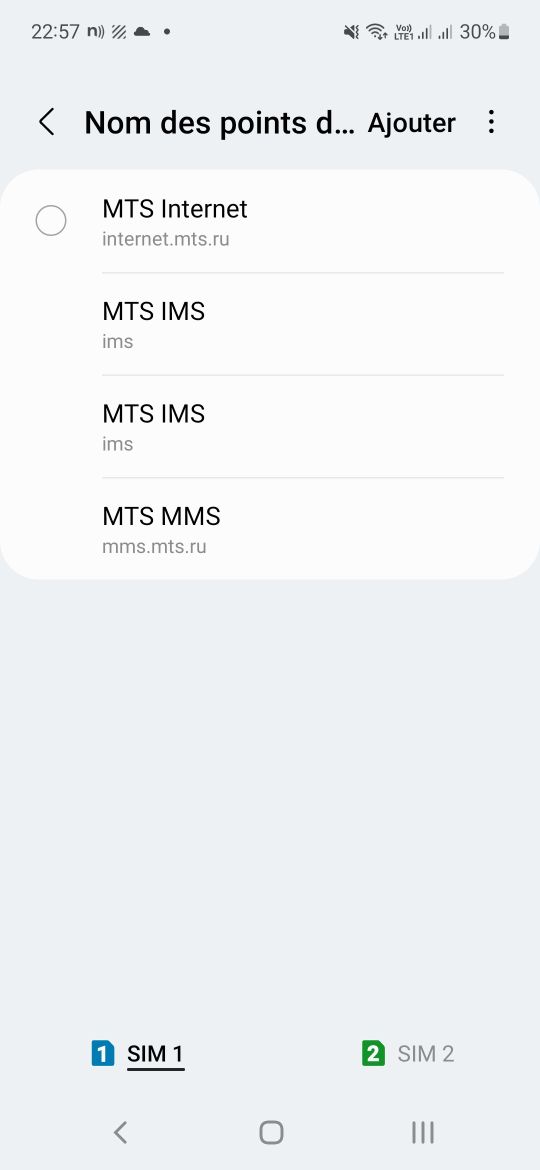
Далее в телефоне открываем раздел «Точки доступа». Нас интересует APN, логин и пароль, которые тоже необходимо узнать и забить.
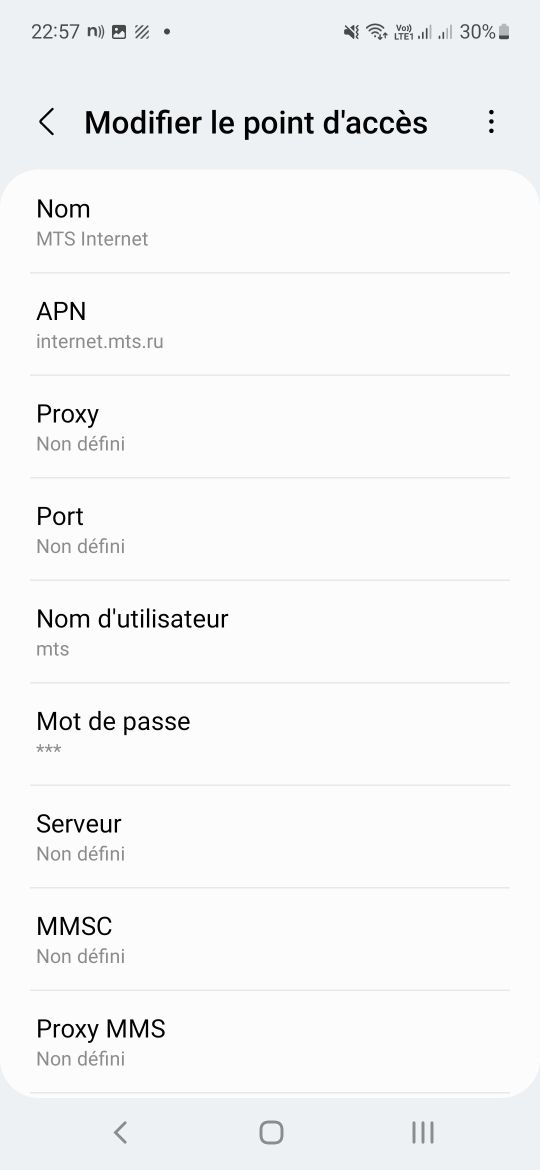
В моём случае параметры оказались такие: APN — internet.mts.ru, логин — mts, пароль — mts.

Также эти данные можно найти в интернете, они есть на сайте любого оператора.
Отдельным пунктом стоит упомянуть IMEI. Обычно он прошивается на заводе и не меняется (либо вообще, либо только с помощью специального софта). Но, как нетрудно догадаться, srsUE является этаким «сферическим в вакууме» девайсом, поэтому IMEI нужно задать самому, например, сгенерировать случайный для любой понравившейся модели телефона.
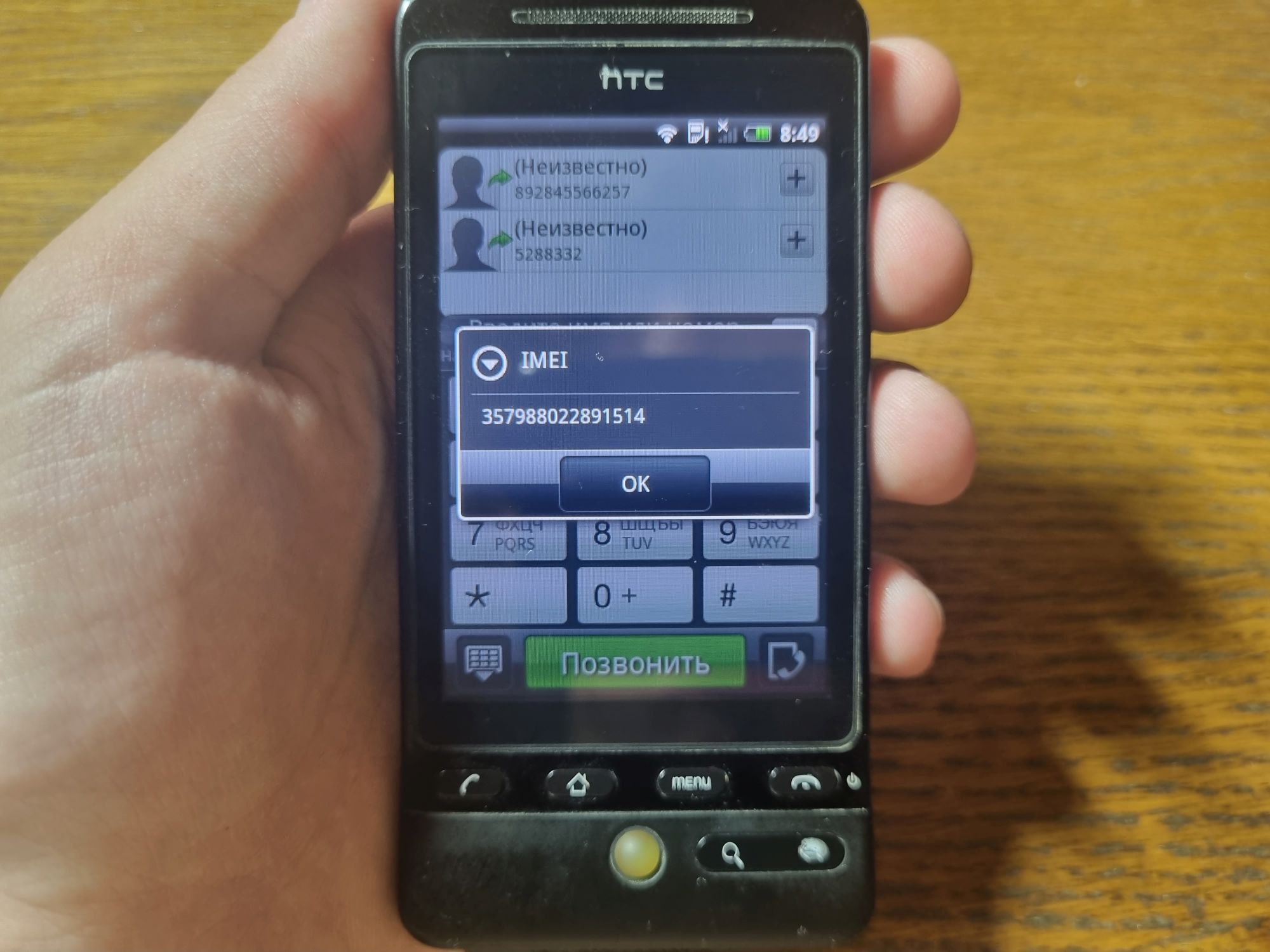
Другим вариантом будет использование IMEI от настоящего телефона. Набираем код *#06#, и на экране появляются заветные цифры. Очень важно: никогда не допускайте одновременной работы srsUE и телефона, IMEI которого вы взяли!
❯ Считыватель
Теперь разберёмся с подключением симки к компьютеру. Для этого понадобится ранее показанный считыватель смарт-карт.
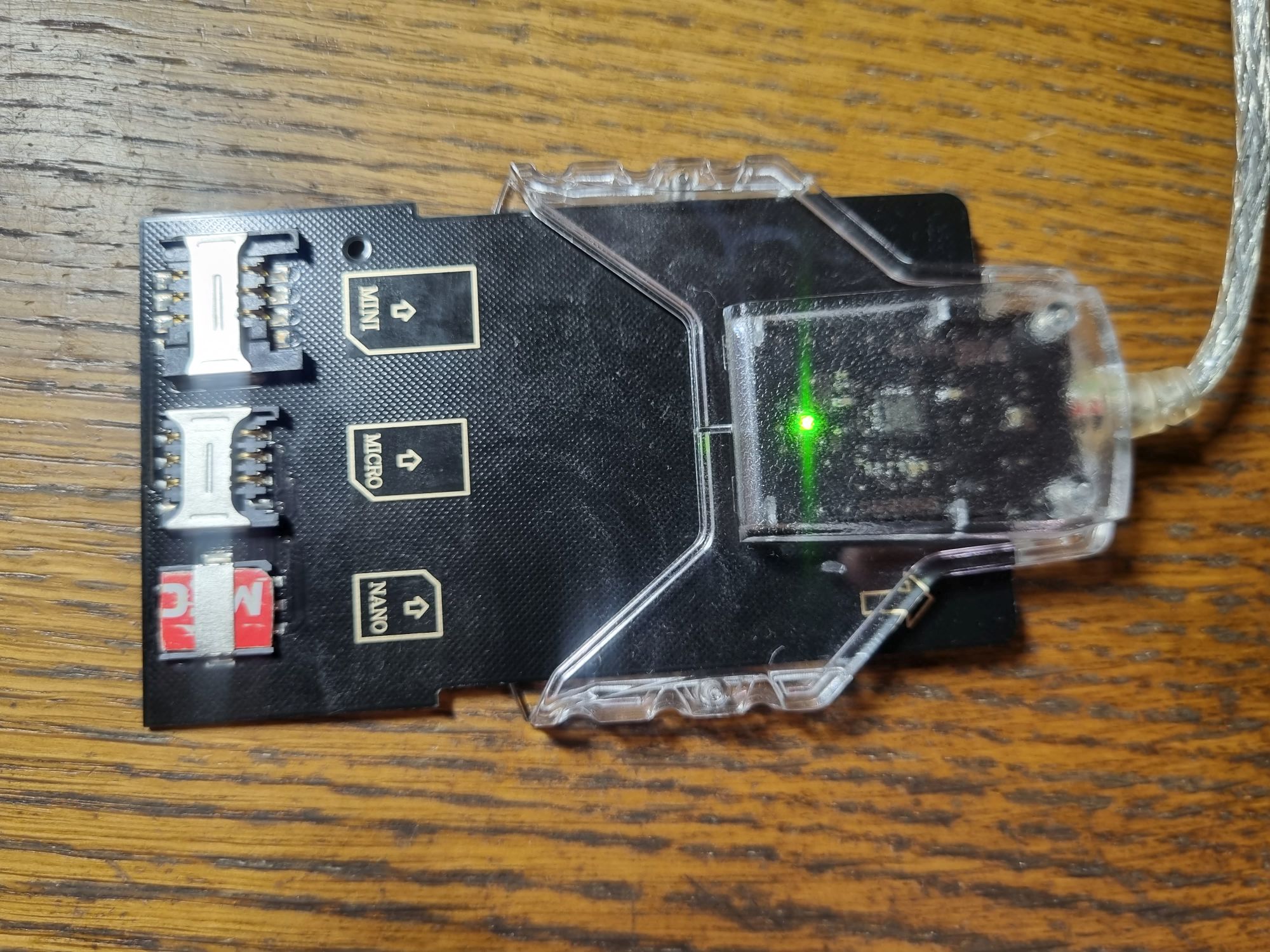
Но есть один нюанс — большинство из них предназначены для полноразмерных карт, отчего потребуется специальный переходник, чтобы вставить в него симку. Если его нет, то берём новую симку и засовываем её вместе с пластмассовой картой.
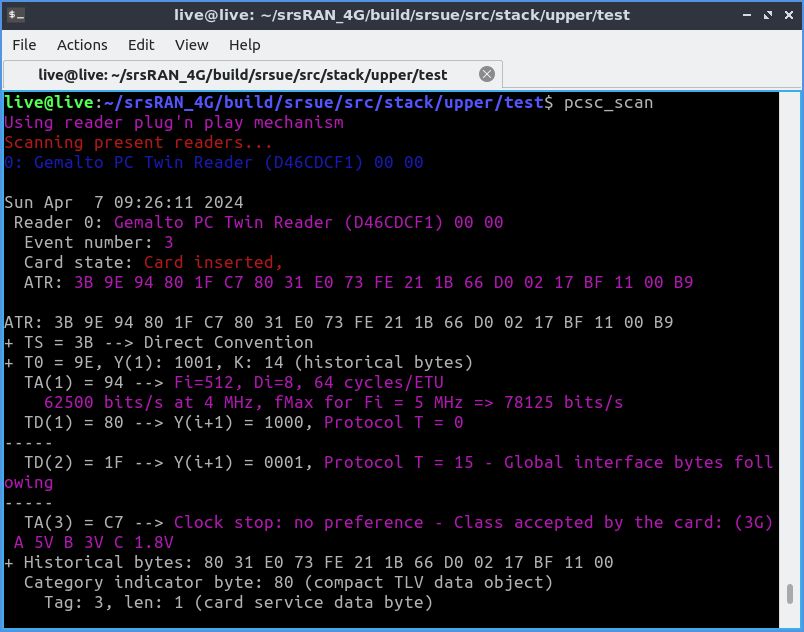
Теперь подключаем считыватель к компу и выполняем следующую команду:
pcsc_scanЕсли софт для работы со смарт-картами установлен правильно, а симка установлена в считыватель, то на экране отобразится примерно следующее:
Двигаемся дальше. Убедимся, что симка работает корректно и читается, для чего переходим в папку с собранным srsRAN и выполняем команды:
cd srsue/src/stack/upper/test
./pcsc_usim_test
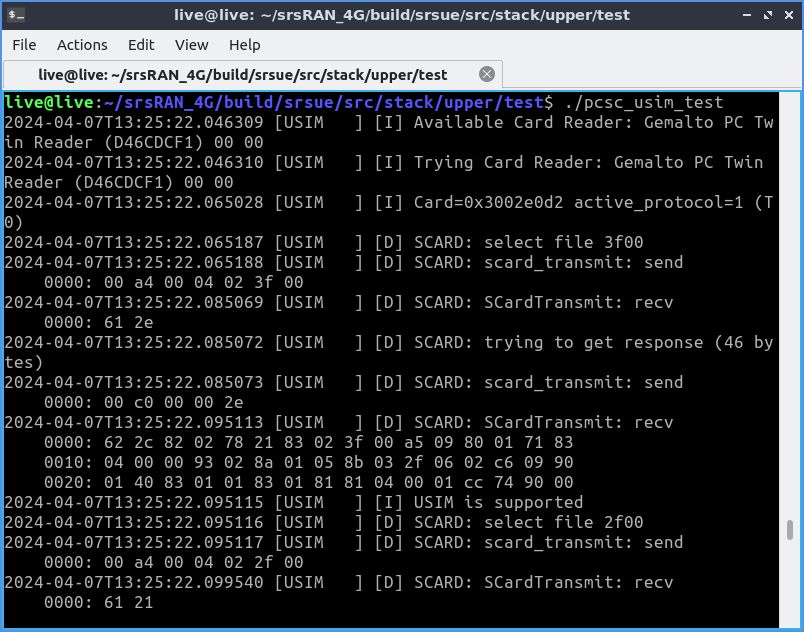
В консоли можно будет увидеть обмен данных с симкой.
❯ Запускаем
Ну что, самое время пробовать. На компьютере отрубаем Wi-Fi и LAN, после чего подключаем SDR и запускаем софт:
cd srsue/src
sudo ./srsue
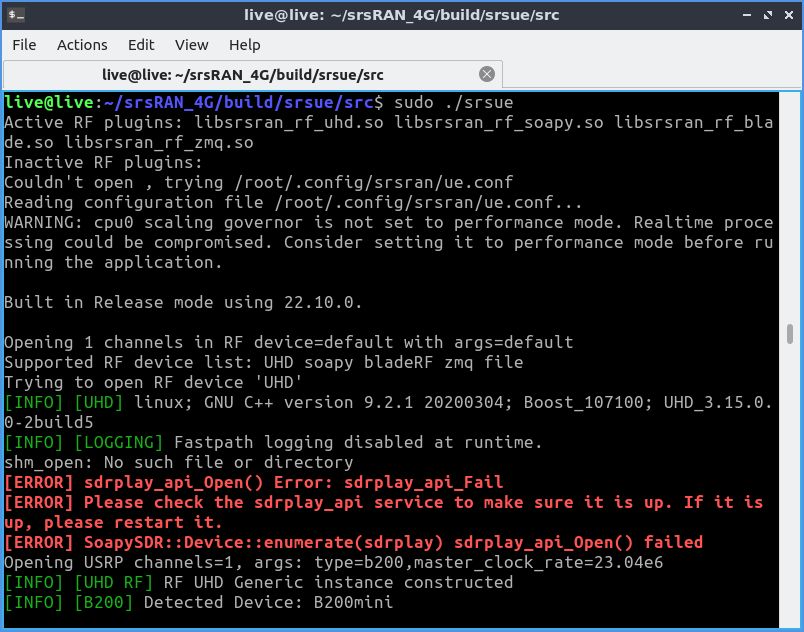
Начнётся стандартная процедуза загрузки прошивки в оперативную память SDR.
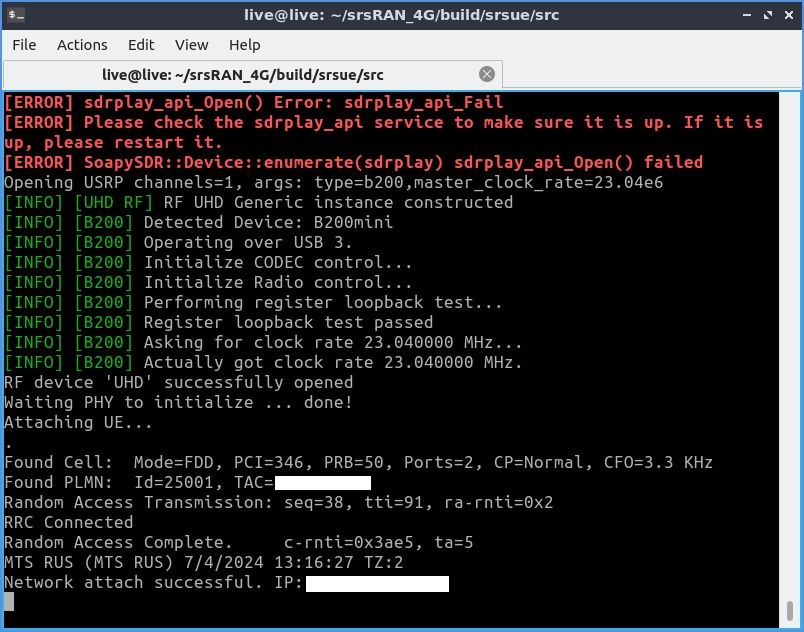
После этого srsUE перейдёт в рабочий режим. И, если всё было сделано правильно, через несколько секунд софт найдёт сеть, а компьютер получит IP-адрес. При этом ОС выдаст уведомление о новом подключении.
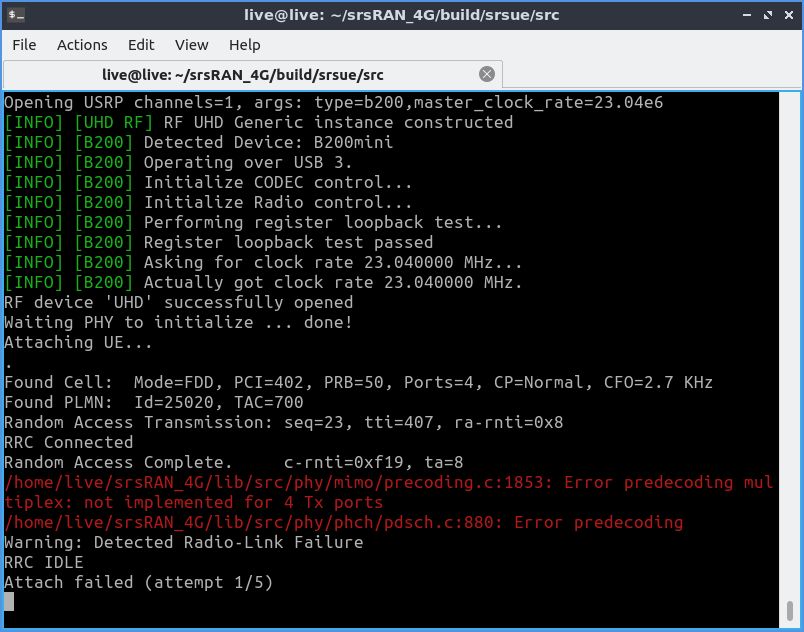
При подключении может возникнуть проблема, что при попытке подключения сеть отваливается. Мне неведомо, с чем это связано, в некоторых источниках удалось выяснить, что причина этому — нехватка пропускной способности SDR. В таком случае нужно попробовать другую вышку или другого оператора (по закону подлости МТС, с которого я только звоню, у меня подключался стабильно, а Теле2, симка которого у меня с пакетом гигабайт, только через раз).
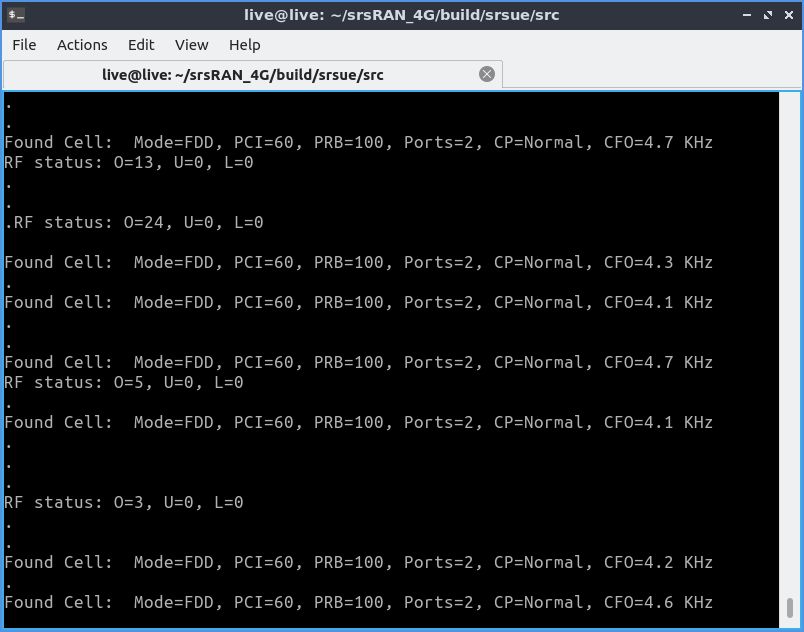
Если в консоли сыпется бесконечное «Found cell...», значит, не проходит аутентификация. В моём случае это было вызвано специально — для проверки я вставил в считыватель дохлую симку.
❯ Доступ в интернет
Теперь, когда подключение работает, можно выйти в сеть.
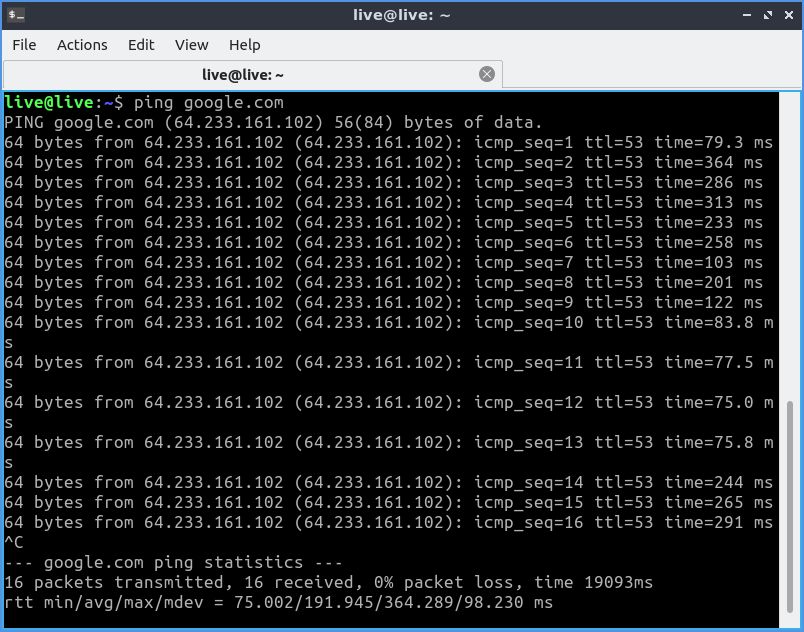
Ping работает успешно.
Да и страницы тоже открываются отлично.
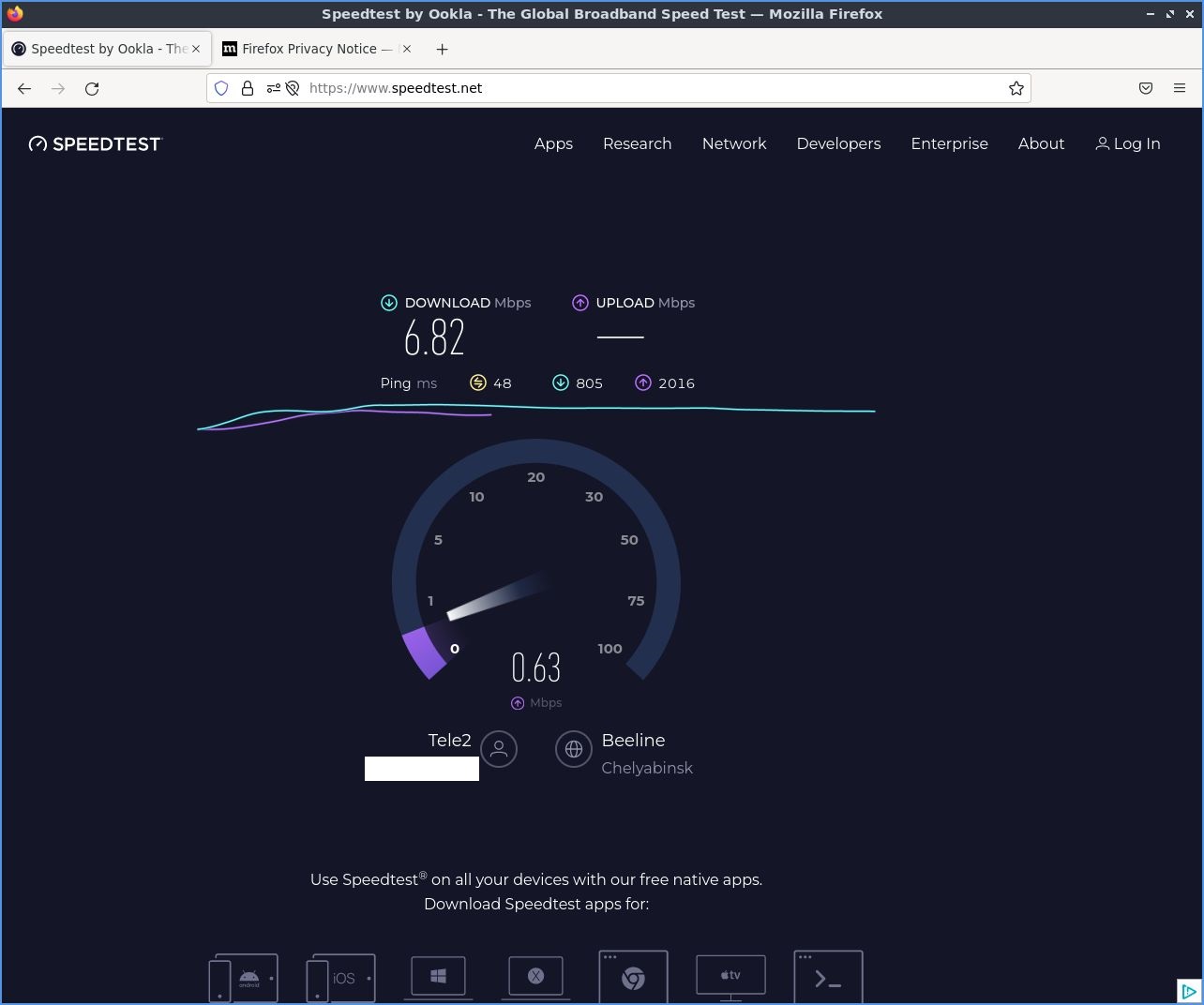
А вот и Speedtest, показывающий, что оператор у меня Tele2, а не домашняя «Интерсвязь».
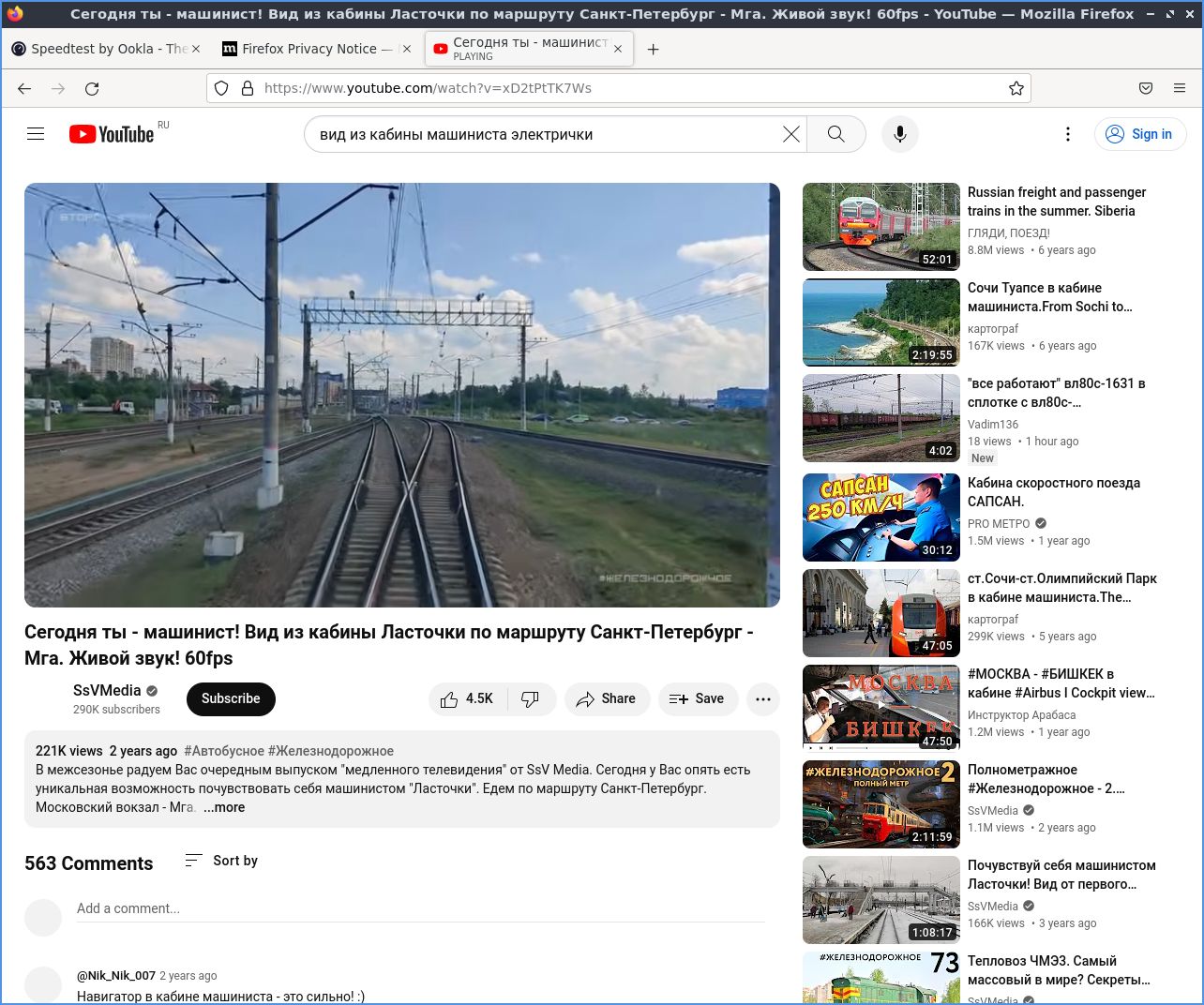
Для проверки стабильности связи я, как и в случае с БС, открыл на компе YouTube и запустил часовое видео в хорошем качестве. Как оказалось, даже на Tele2 при успешном подключении сеть ловится весьма приемлемо.
❯ Вот как-то так
Как и ожидалось, подключить компьютер к интернету при помощи обычного SDR оказалось даже проще, чем поднять сеть. Коммерческие БС имеют хороший сигнал, поэтому сеть нормально ловится даже с не слишком хорошими антеннами. Впрочем, как оказалось, некоторые нюансы (увы, не зависящие от нас) всё равно есть, так что в идеале запастись симками сразу нескольких операторов: хоть один точно заработает. В остальном же это полностью рабочая реализация сотового модема, которую не составляет труда запустить при наличии оборудования.
Такие дела.
Автор: Лев






