Введение
В предыдущей статье я только начинал работать с Arduino, в результате чего закономерно получилась метеостанция. В этой статье пойдём дальше — будем делать аутентификацию с помощью RFID карт и Arduino в приложении InterSystems Caché.
Передача аутентификации
В Caché есть механизм делегирования аутентификации — передачи процесса аутентификации пользовательскому коду. Чтобы его включить, надо сделать следующее:
- Написать код аутентификации пользователей в рутине ZAUTHENTICATE. У неё есть 4 точки входа: получения логина/пароля, их проверка и назначение прав, смена пароля, формирование токена. Подробнее об этом ниже.
- Включить передачу аутентификации в Caché (SMP → System Administration → Security → System Security → Authentication/CSP Session Options, установите флаг Allow Delegated authentication и сохраните настройки).
- Включить передачу аутентификации для требуемых сервисов (SMP → Menu → Manage Services → Сервис → Allowed Authentication Methods → выбрать Delegated → Save) и/или приложений (SMP → Menu → Manage Web Applications → Приложение → Allowed Authentication Methods → выбрать Delegated → Save).
Как это работает
Вот что происходит, когда пользователь аутентифицируется в сервисе или веб-приложении, для которого включена передача аутентификации:
- Вызывается рутина ZAUTHENTICATE. Код этой рутины пишется пользователем и может быть любым Caché ObjectScript кодом, в том числе и $ZF вызовы.
- Следующий шаг зависит от того, был ли успешным вызов ZAUTHENTICATE:
- Если вызов ZAUTHENTICATE успешен и это первый раз, когда данный пользователь аутентифицируется с ZAUTHENTICATE, то для него создаётся запись пользователя типа “Delegated user”. Если ZAUTHENTICATE назначает пользователю права или другие свойства, они становятся соответствующими свойствами пользователя.
- Если вызов ZAUTHENTICATE успешен и это не первый раз, когда данный пользователь аутентифицируется с ZAUTHENTICATE, то его запись пользователя обновляется.
- Если вызов ZAUTHENTICATE не успешен, пользователю выдаётся ошибка доступа.
- Если для инстанса и сервиса включена двухфакторная аутентификация, то производится поиск номера телефона пользователя и оператора. Если они заданы, происходит двухфакторная аутентификация, если нет — юзер не аутентифицируется.
- Делегированный пользователь отображается в таблице пользователей.
Откуда пользователи?
Есть два метода аутентификации в зависимости от того какие способы аутентификации включены для приложения/сервиса:
- Delegated — имя/пароль берутся из GetCredentials, проверяются средствами ZAUTHENTICATE (тип пользователя — делегированный).
- Delegated и Password — имя/пароль берутся из GetCredentials, проверяются стандартными механизмами Caché (тип пользователя — Caché).
Теперь перейдём к рассмотрению рутины ZAUTHENTICATE и её точек входа.
ZAUTHENTICATE
Эта основная рутина, содержащая 4 точки входа.
▍GetCredentials
Эта точка входа вызывается в том случае, когда передача аутентификации включена для сервиса, и она вызывается вместо запроса логина/пароля у пользователя. Код этой рутины устанавливает логин и пароль (любым способом). Впоследствии (вне этой рутины) полученные логин и пароль аутентифицируются, будто пользователь их ввёл как обычно. Метод получения логина и пароля может быть любой — ввод с клавиатуры, API, считывание внешнего устройства — в этой статье будем использовать аутентификацию с помощью RFID карты.
Данная точка входа возвращает статус, и если это ошибка, то она будет записана в аудит, а попытка аутентификации будет отклонена. Исключение — ошибка $SYSTEM.Status.Error($$$GetCredentialsFailed), в таком случае пользователю предложат ввести логин/пароль стандартным методом Caché. Сигнатура следующая:
GetCredentials(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials) Public { }Где:
- ServiceName — название сервиса, через который идёт подключение
- Namespace — область, если указана при подключении
- Username — имя пользователя
- Password — пароль
- Credentials — в настоящее время не используется
Отмечу важную особенность этой точки входа. Если для сервиса/приложения включена и передача аутентификации и обычная аутентификация по паре логин/пароль (Password Authentication), то логин и пароль, полученные через GetCredentials, будут использованы для стандартной аутентификации по паролю.
▍ZAUTHENTICATE
В случае если первоначальная аутентификация успешна, ZAUTHENTICATE устанавливает роли и другие свойства пользователя. В случае если это не первая аутентификация, свойства могут быть изменены. Для этого в коде рутины устанавливаются свойства массива Properties. Сигнатура:
ZAUTHENTICATE(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials, Properties) Public { }
Массив Properties:
- Properties("Comment") — комментарий
- Properties("FullName") — имя и фамилия
- Properties("NameSpace") — стартовая область
- Properties("Roles") — список ролей через запятую
- Properties("Routine") — стартовая рутина
- Properties("Password") — пароль
- Properties("Username") — имя пользователя
- Properties("PhoneNumber") — телефонный номер пользователя
- Properties("PhoneProvider") — оператор телефона
- Properties("AutheEnabled") — включить стандартную двухфакторную аутентификацию (для этого надо установить значение, равное $$$AutheTwoFactorSMS)
▍ChangePassword
Точка входа для смены пароля пользователя. Сигнатура следующая:
ChangePassword(Username, NewPassword, OldPassword, Status) Public { }Где:
- NewPassword — новый пароль
- OldPassword — старый пароль
- Status — результат операции изменения пароля
▍SendTwoFactorToken
Для использования в стандартной двухфакторной аутентификации. Определяет формат запроса и токена аутентификации. Сигнатура:
SendTwoFactorToken(Username, ServiceName,Namespace,Application,Credentials,SecurityToken,TwoFactorTimeout,UserPhoneNumber) Public { }Где:
- Application — CSP приложение или рутина, к которой подключается пользователь
- SecurityToken — токен, который будет отправлен пользователю
- TwoFactorTimeout — время действия токена
- UserPhoneNumber — телефонный номер пользователя
Пример
Для начала покажу простейший пример для терминала Caché в Windows — сервиса %Service_Console, который будет спрашивать логин и пароль у пользователя. Включим передачу аутентификации в системе для этого сервиса. После этого напишем рутину ZAUTHENTICATE (в области %SYS):
ZAUTHENTICATE(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials, Properties) PUBLIC {
#Include %occErrors
#Include %occStatus
Quit $$$OK
}
GetCredentials(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials) Public {
#Include %occErrors
#Include %occStatus
Do ##class(%Prompt).GetString("USER:",.Username)
Do ##class(%Prompt).GetString("PASS:",.Password)
Quit $$$OK
}В терминале это будет выглядеть аналогично обычному логину.
>USER: _SYSTEM
>PASS: SYSRFID
Перейдём к аутентификации на RFID. Идея состоит в следующем — из Caché сделаем возможность записывать в зашифрованном виде информацию на карточку, а при аутентификации будем её считывать, расшифровывать и возвращать на проверку.
Для начала соберём схему из Arduino Uno и модуля RFID-RC522:
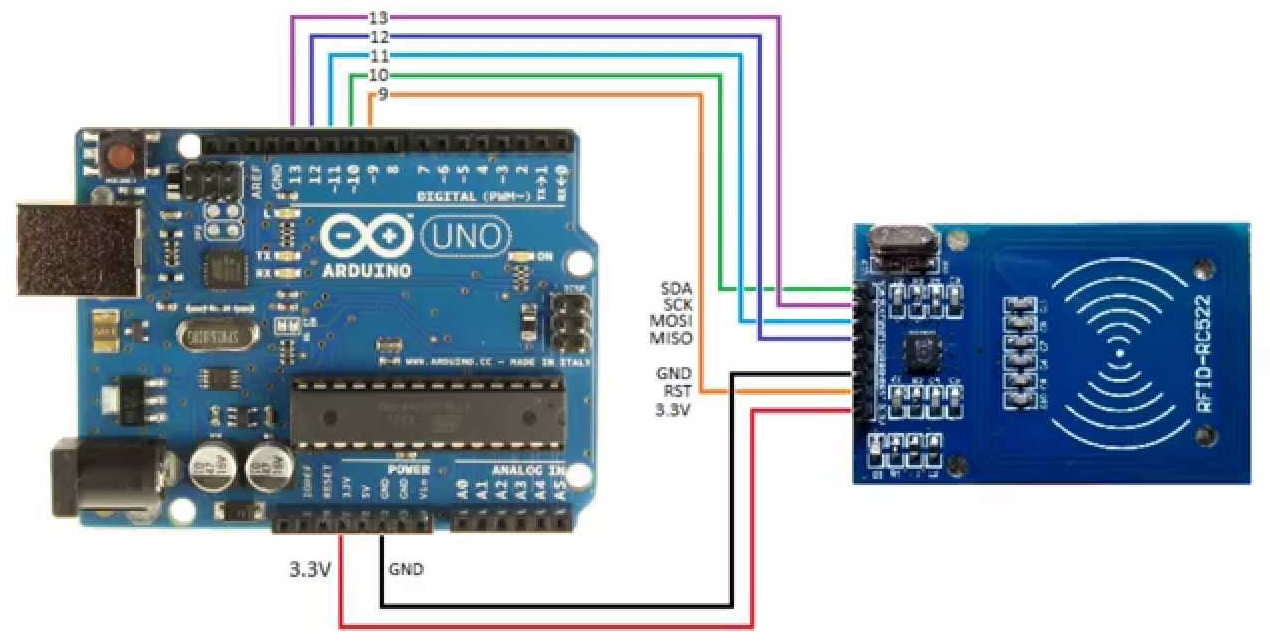
Вот код на С, использующий библиотеку MF522 (там же есть распиновка для других моделей Arduino). Он по COM порту принимает 2 команды:
- Get — по ней на com порт передаётся содержимое блоков RFID карты 2, 4, 5, 6
- Set@bloc2@bloc4@bloc5@bloc6 — по ней содержимое блоков 2, 4, 5, 6 на карте перезаписывается пришедшими данными
#include <SPI.h> //include the SPI bus library
#include <MFRC522.h> //include the RFID reader library
#define SS_PIN 10 //slave select pin
#define RST_PIN 9 //reset pin
#define u1b 2 //Block on a card for user1 byte array
#define u2b 4 //Block on a card for user2 byte array
#define p1b 5 //Block on a card for pass1 byte array
#define p2b 6 //Block on a card for pass2 byte array
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // instatiate a MFRC522 reader object.
MFRC522::MIFARE_Key key; //create a MIFARE_Key struct named 'key', which will hold the card information
byte readbackblock[18]; //This array is used for reading out a block. The MIFARE_Read method requires a buffer that is at least 18
String inString = ""; // COM port incoming data buffer
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communications with the PC
SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus
mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522 card (in case you wonder what PCD means: proximity coupling device)
// Serial.println("Scan a MIFARE Classic card");
// Prepare the security key for the read and write functions - all six key bytes are set to 0xFF at chip delivery from the factory
// Since the cards in the kit are new and the keys were never defined, they are 0xFF
// if we had a card that was programmed by someone else, we would need to know the key to be able to access it.
// This key would then need to be stored in 'key' instead.
for (byte i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
key.keyByte[i] = 0xFF; // keyByte is defined in the "MIFARE_Key" 'struct' definition in the .h file of the library
}
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
// Receive data from com port
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
int inChar = Serial.read();
if (inChar != 'n') {
inString += (char)inChar;
} else {
// New line
while (!initCard()); // connect to an RFID card
String Action = inString.substring(0, 3);
if (Action == "Set") {
// Write login and pass into the card
setUserAndPassToCard(inString);
} else if (Action == "Get") {
// Read login and pass from the card
readUserAndPassToCom();
} else {
Serial.println(Action);
}
disconnectCard(); // disconnect RFID card
inString = "";
}
}
}
/// Read blocks with user/pass info and output the to COM port:
/// user1user2@pass1pass2
void readUserAndPassToCom()
{
readBlockToCom(u1b);
readBlockToCom(u2b);
Serial.write("@");
readBlockToCom(p1b);
readBlockToCom(p2b);
Serial.println("");
}
/// Set user/pass info into a card
/// Data: Set@user1@user2@pass1@pass2
/// Data sample: Set@1234567890123456@1234567890123456@1234567890123456@1234567890123456
void setUserAndPassToCard(String Data) {
// Serial.println(Data);
byte user1[16], user2[16], pass1[16], pass2[16];
String user1str = inString.substring(4, 20);
String user2str = inString.substring(21, 37);
String pass1str = inString.substring(38, 54);
String pass2str = inString.substring(55, 71);
stringToArray(user1str, user1, sizeof(user1));
stringToArray(user2str, user2, sizeof(user2));
stringToArray(pass1str, pass1, sizeof(pass1));
stringToArray(pass2str, pass2, sizeof(pass2));
writeBlock(u1b, user1); // u1b is the block number, user1 is the block content
writeBlock(u2b, user2);
writeBlock(p1b, pass1);
writeBlock(p2b, pass2);
Serial.println("Done");
}
void stringToArray(String str, byte array[], int arrlength)
{
for (int j = 0 ; j < arrlength ; j++)
{
array[j] = str.charAt(j);
}
}
bool initCard()
{
// Look for new cards (in case you wonder what PICC means: proximity integrated circuit card)
if ( ! mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent()) {//if PICC_IsNewCardPresent returns 1, a new card has been found and we continue
return false; //if it did not find a new card is returns a '0' and we return to the start of the loop
}
// Select one of the cards
if ( ! mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) {//if PICC_ReadCardSerial returns 1, the "uid" struct (see MFRC522.h lines 238-45)) contains the ID of the read card.
return false; //if it returns a '0' something went wrong and we return to the start of the loop
}
return true;
}
void disconnectCard()
{
// Halt PICC
mfrc522.PICC_HaltA();
// Stop encryption on PCD
mfrc522.PCD_StopCrypto1();
}
void readBlockToCom(int number)
{
readBlock(number, readbackblock);//read the block back
for (int j = 0 ; j < 16 ; j++) //print the block contents
{
Serial.write (readbackblock[j]);//Serial.write() transmits the ASCII numbers as human readable characters to serial monitor
}
}
int writeBlock(int blockNumber, byte arrayAddress[])
{
// this makes sure that we only write into data blocks. Every 4th block is a trailer block for the access/security info.
int largestModulo4Number = blockNumber / 4 * 4;
int trailerBlock = largestModulo4Number + 3; //determine trailer block for the sector
if (blockNumber > 2 && (blockNumber + 1) % 4 == 0) {
Serial.print(blockNumber); //block number is a trailer block (modulo 4); quit and send error code 2
Serial.println(" is a trailer block:");
return 2;
}
//Serial.print(blockNumber);
//Serial.println(" is a data block:");
/*****************************************authentication of the desired block for access***********************************/
byte status = mfrc522.PCD_Authenticate(MFRC522::PICC_CMD_MF_AUTH_KEY_A, trailerBlock, &key, &(mfrc522.uid));
// byte PCD_Authenticate(byte command, byte blockAddr, MIFARE_Key *key, Uid *uid);
// this method is used to authenticate a certain block for writing or reading
// command: See enumerations above -> PICC_CMD_MF_AUTH_KEY_A = 0x60 (=1100000),
// this command performs authentication with Key A
// blockAddr is the number of the block from 0 to 15.
// MIFARE_Key *key is a pointer to the MIFARE_Key struct defined above, this struct needs to be defined for each block.
// New cards have all A/B= FF FF FF FF FF FF
// Uid *uid is a pointer to the UID struct that contains the user ID of the card.
if (status != MFRC522::STATUS_OK) {
Serial.print("PCD_Authenticate() failed: ");
Serial.println(mfrc522.GetStatusCodeName(status));
return 3;//return "3" as error message
}
// it appears the authentication needs to be made before every block read/write within a specific sector.
// If a different sector is being authenticated access to the previous one is lost.
/*****************************************writing the block***********************************************************/
status = mfrc522.MIFARE_Write(blockNumber, arrayAddress, 16);
//valueBlockA is the block number, MIFARE_Write(block number (0-15), byte array containing 16 values, number of bytes in block (=16))
// status = mfrc522.MIFARE_Write(9, value1Block, 16);
if (status != MFRC522::STATUS_OK) {
Serial.print("MIFARE_Write() failed: ");
Serial.println(mfrc522.GetStatusCodeName(status));
return 4;//return "4" as error message
}
//Serial.println("block was written");
}
int readBlock(int blockNumber, byte arrayAddress[])
{
int largestModulo4Number = blockNumber / 4 * 4;
int trailerBlock = largestModulo4Number + 3; //determine trailer block for the sector
/*****************************************authentication of the desired block for access********************************************/
byte status = mfrc522.PCD_Authenticate(MFRC522::PICC_CMD_MF_AUTH_KEY_A, trailerBlock, &key, &(mfrc522.uid));
// byte PCD_Authenticate(byte command, byte blockAddr, MIFARE_Key *key, Uid *uid);
// this method is used to authenticate a certain block for writing or reading
// command: See enumerations above -> PICC_CMD_MF_AUTH_KEY_A = 0x60 (=1100000),
// this command performs authentication with Key A
// blockAddr is the number of the block from 0 to 15.
// MIFARE_Key *key is a pointer to the MIFARE_Key struct defined above, this struct needs to be defined for each block.
// New cards have all A/B= FF FF FF FF FF FF
// Uid *uid is a pointer to the UID struct that contains the user ID of the card.
if (status != MFRC522::STATUS_OK) {
Serial.print("PCD_Authenticate() failed (read): ");
Serial.println(mfrc522.GetStatusCodeName(status));
return 3;//return "3" as error message
}
// it appears the authentication needs to be made before every block read/write within a specific sector.
// If a different sector is being authenticated access to the previous one is lost.
/*****************************************reading a block***********************************************************/
byte buffersize = 18;//we need to define a variable with the read buffer size, since the MIFARE_Read method below needs a pointer to the variable that contains the size...
status = mfrc522.MIFARE_Read(blockNumber, arrayAddress, &buffersize);//&buffersize is a pointer to the buffersize variable; MIFARE_Read requires a pointer instead of just a number
if (status != MFRC522::STATUS_OK) {
Serial.print("MIFARE_read() failed: ");
Serial.println(mfrc522.GetStatusCodeName(status));
return 4;//return "4" as error message
}
}Класс Arduino.Delegate, который имеет 2 точки входа:
- SetCredentials — принимает на вход логин и пароль, шифрует их AES шифрованием с помощью ключа хранящегося в системе и записывает на RFID карту.
- GetCredentials — получает шифротекст с карты и расшифровывает его, возвращая логин, пароль и статус операции.
/// Delegated Authentication with Arduino.
/// Installation steps:<br>
/// 1. Connect arduino (and upload C code from Delegated.ino there)<br>
/// 2. Make this class visible in %SYS namespace (import there or map pckage)<br>
/// 3. Set SerialPort parameter to a correct value and recompile the class<br>
/// 4. Run <example>Do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).InitEncryption(Key, IV)</example>
/// 5. Write encrypted user credentials to RFID card with SetCredentials<br>
/// 6. Import ZAUTHENTICATE into %SYS<br>
/// 7. Enable Delegated and password auth for relevant services and/or apps
Class Arduino.Delegated [ Abstract ]
{
Parameter SerialPort As %String = "com3";
/// Creates managed encryption key.<br>
/// key - Input key material.
/// Key material 16, 24, or 32 characters long (on Unicode systems, with all character values < 256) is used directly.
/// Otherwise, Password-Based Key Derivation Function #2 (PBKDF2)
/// is used with HMAC-SHA-1,
/// no salt, and one iteration
/// to generate an AES key of the next larger valid size (up to 32 bytes).
/// (See RSA Laboratories Public-Key Cryptography Standards #5 for more information.)
/// <br><br>
/// IV - Initialization vector (optional).
/// If this argument is present it must be 16 characters long (on Unicode systems, with all character values < 256).
/// If this argument is omitted (or is an empty string), a null initialization vector is used.
/// <br>
/// <example>Do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).Init("", "")</example>
ClassMethod Init(Key As %String, IV As %String)
{
New $Namespace
Set $Namespace = "%SYS"
Set ^Arduino("Key")= Key
Set ^Arduino("IV")= IV
}
/// Send Arduino the command to set credentials on a card to Username/Password (encrypted)
/// <example>Do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).SetCredentials("_SYSTEM", "SYS")</example>
ClassMethod SetCredentials(Username As %String(MAXLEN=15), Password As %String(MAXLEN=15)) As %Status
{
Set Status = $$$OK
Set CipherUsername = ..EncryptText(Username)
Set CipherPassword = ..EncryptText(Password)
Set User1 = $Extract(CipherUsername, 1, 16)
Set User2 = $Extract(CipherUsername, 17, 32)
Set User2 = ..AppendToString(User2, , 16)
Set Pass1 = $Extract(CipherPassword, 1, 16)
Set Pass2 = $Extract(CipherPassword, 17, 32)
Set Pass2 = ..AppendToString(Pass2, , 16)
Set CommandList = $ListBuild("Set", User1, User2, Pass1, Pass2)
Set Command = $ListToString(CommandList, "@")
Set Status = ..ExecuteCommand(.Command)
If (Status = "Done") {
Set Status = $$$OK
} Else {
Set Status = $$$ERROR($$$GeneralError, "SetCredentials failure, received: " _ Status)
}
Return Status
}
/// Connect to an Arduino device, receive credentials, decode them and set to Username/Password variables.
/// <example>do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).GetCredentials(.Username, .Password)</example>
ClassMethod GetCredentials(Output Username As %String, Output Password As %String) As %Status
{
Kill Username, Password
Set Username = ""
Set Password = ""
Set Status = $$$OK
Set Credentials = ..ExecuteCommand("Get")
If (($L(Credentials) =65) && ($L(Credentials,"@") = 2)) {
Set CipherUsername = $Piece(Credentials, "@", 1)
Set CipherPassword = $Piece(Credentials, "@", 2)
Set CipherUsername = $Extract(CipherUsername, 1, 24) // we need only first 24 characters
Set CipherPassword = $Extract(CipherPassword, 1, 24)
Set Username = ..DecryptText(CipherUsername)
Set Password = ..DecryptText(CipherPassword)
} Else {
Set Status = $$$ERROR($$$GeneralError, "GetCredentials failure, received: " _ Credentials)
}
Return Status
}
/// Send one line at a time, using common terminating characters (i.e., CR) and receive output
/// Possible comands:<br>
/// <b>Get</b> - reads an RFID card and returns information in a format: user@pass<br>
/// <b>Set@user1@user2@pass1@pass2</b> - sets information on a RFID card
/// in a format: user@pass (where user = user1@user2)<br>
/// Returns output, produced by Arduino
/// <example>w ##class(Arduino.Delegated).ExecuteCommand("Get")</example>
ClassMethod ExecuteCommand(ByRef Command As %String, SerialPort = {..#SerialPort}) As %String
{
set x=""
try {
//Parameters used to open the serial device:
// portstate = " 0801n0" - by byte position:
// 1: space indicates "don't disconnect the port"
// 2: 0 indicates "don't use modem control"
// 3: 8 indicates 8 data bits
// 4: 0 indicates no parity
// 5: 1 indicates one stop bit
// 6: n indicates that flow control is disabled
// 7: 0 indicates disable DTR
// /BAUD=9600 determines the baud rate, of course.
open SerialPort:(:::" 0801n0":/BAUD=9600)
set old = $io //Keep track of the original device
use SerialPort
write $char(10)
hang 1
write Command _ $Char(10)
read x //Read until a termination character is reached
use old
close SerialPort
} catch ex {
close SerialPort
w $System.Status.GetErrorText(ex.AsStatus())
}
return x
}
/// Get key to encode/decode via EncryptText/DecryptText
ClassMethod GetKey() [ CodeMode = expression ]
{
$Get(^Arduino("Key"))
}
/// Get IV to encode/decode via EncryptText/DecryptText
ClassMethod GetIV() [ CodeMode = expression ]
{
$Get(^Arduino("IV"))
}
/// Encrypt PlainText with AESCBCEncrypt
/// <example>Write ##class(Arduino.Delegated).EncryptText("string")</example>
ClassMethod EncryptText(PlainText As %String) As %String
{
Set Text=$ZConvert(PlainText,"O","UTF8")
Set Text=$System.Encryption.AESCBCEncrypt(Text, ..GetKey(), ..GetIV())
Set Ciphertext=$System.Encryption.Base64Encode(Text)
Return Ciphertext
}
/// Decrypt PlainText with AESCBCEncrypt
/// <example>Write ##class(Arduino.Delegated).DecryptText("sFgKzZVle187N4OqhhcXPw==")</example>
ClassMethod DecryptText(CipherText As %String) As %String
{
Set Text=$System.Encryption.Base64Decode(CipherText)
Set Text=$System.Encryption.AESCBCDecrypt(Text, ..GetKey(), ..GetIV())
Set PlainText=$ZConvert(Text,"I","UTF8")
Return PlainText
}
/// Extends right side of a String by Character up to Length chars
/// <example>Write ##class(Arduino.Delegated).AppendToString("")</example>
ClassMethod AppendToString(String As %String, Character As %String(MAXLEN=1) = "_", Length As %Integer = {$Length(String)}) As %String
{
Set Difference = Length - $Length(String)
Return:Difference<=0 String
Set Tail = $Justify("", Difference)
Set Tail = $Translate(Tail, " ", Character)
Return String _ Tail
}
}Рутина ZAUTHENTICATE, которая вызывает класс Arduino.Delegated, метод GetCredentials:
ZAUTHENTICATE(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials, Properties) PUBLIC {
#Include %occStatus
Quit $$$OK
}
GetCredentials(ServiceName, Namespace, Username, Password, Credentials) Public {
#Include %occErrors
#Include %occStatus
Quit ##class(Arduino.Delegated).GetCredentials(.Username, .Password)
}Готово! Собранное устройство выглядит вот так:

Устанавливаем ключи шифрования в терминале, области %SYS (там должен быть доступен класс Arduino.Delegated):
Do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).InitEncryption(Key, IV)Где Key — ключ шифрования, IV — вектор инициализации. Они будут использоваться для шифрования логина и пароля. Подключаем Arduino к Caché и записываем на карточку информацию для аутентификации командой:
Do ##class(Arduino.Delegated).SetCredentials("_SYSTEM", "SYS")Включаем аутентификацию Delegated и Password в нужных сервисах/веб-приложениях и можно аутентифицироваться (например, в терминале или портале управления системой) поднося карту к считывателю RFID карт.
Возможные улучшения
- Повышение уровня безопасности с помощью использования управляемых ключей шифрования для шифрования логина и пароля.
- Повышение уровня безопасности с помощью использования двухфакторной аутентификации — сначала получать пару логин/пароль, а потом считывать карту, на которой хранится ключ, уникальный для пользователя. Затем нужно сверять полученный ключ с тем, который хранится в системе для данного пользователя. Варианты хранения произвольных данных пользователя обсуждались на Community портале InterSystems.
- Добавить возможность хранения логина и пароля длиннее 15 символов каждый.
Выводы
Гибкая система аутентификации Caché позволяет реализовать произвольную логику аутентификации пользователей.
Ссылки
» Документация
» GitHub репозиторий с кодом (в области SAMPLES есть пример рутины ZAUTHENTICATE)
Автор: InterSystems






