Спешу поделиться с коллегами накопленным опытом при разработке для Android Wear.
Все важные моменты проще всего показать на примере приложения, которое показывает уровень заряда батареи на часах и смартфоне.
Загрузим Android Studio.
Создадим новый проект:
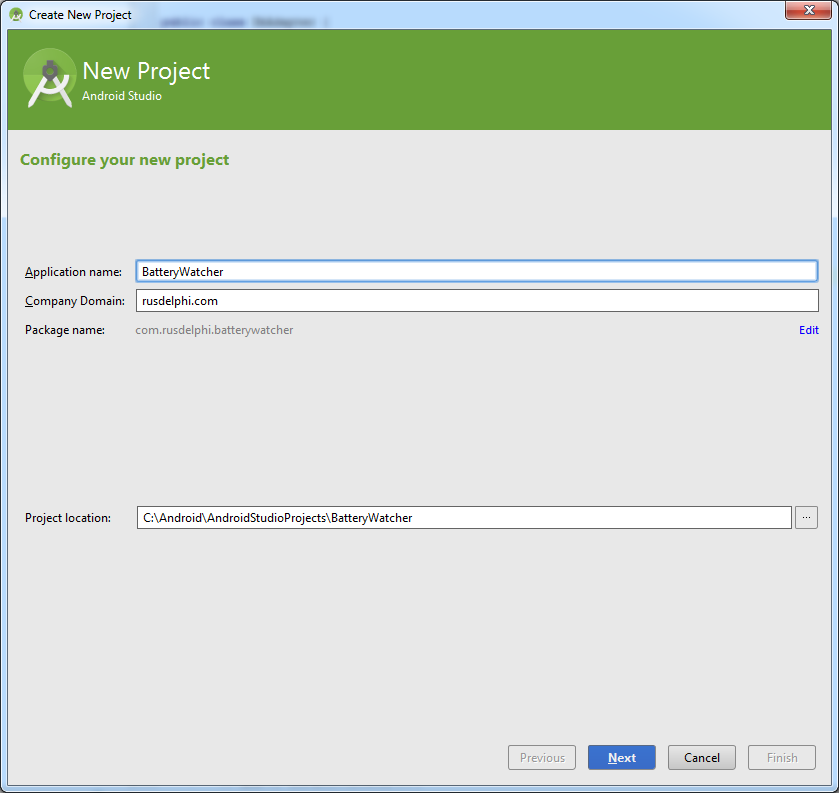
Выбираем оба устройства:
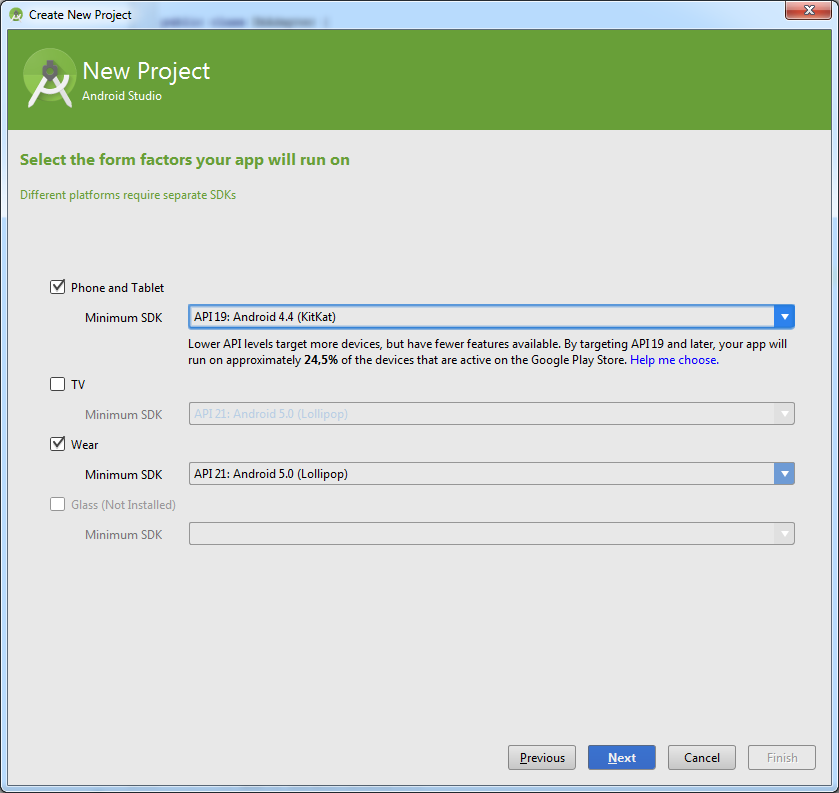
Далее все стандартно:
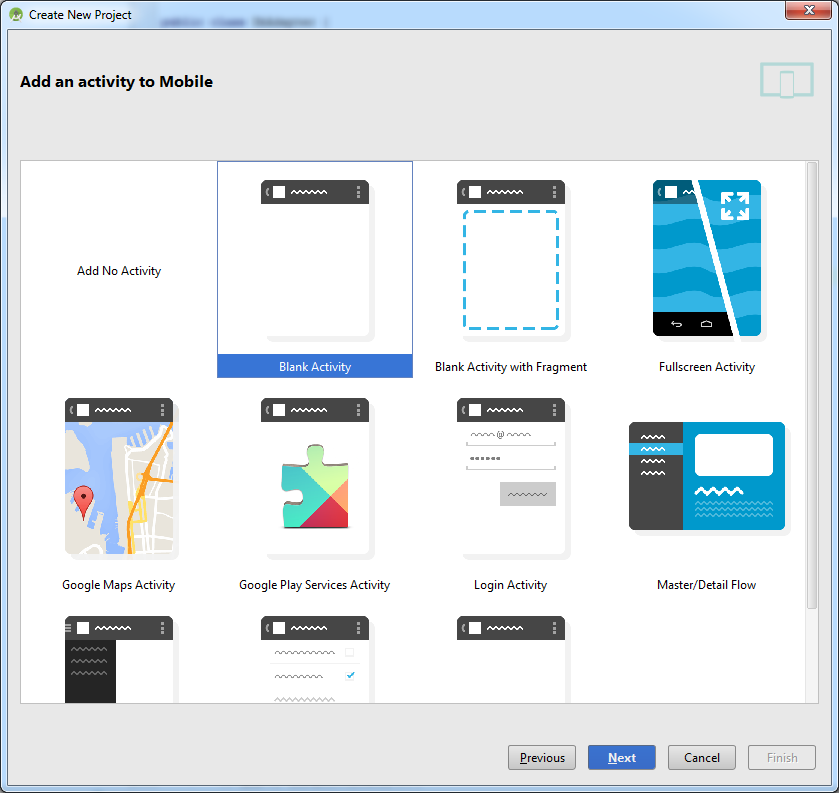
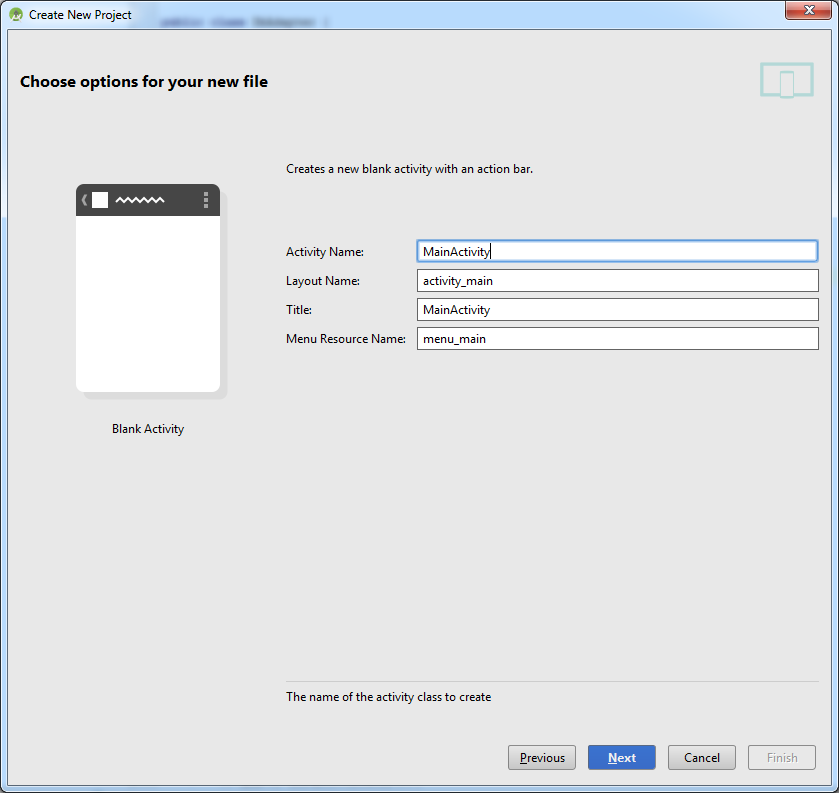
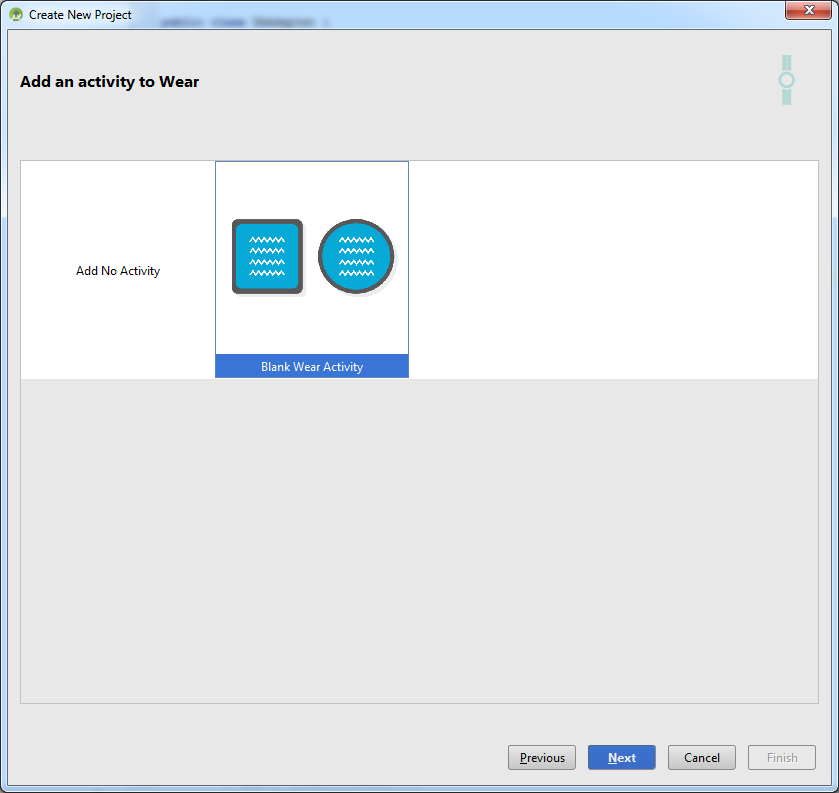
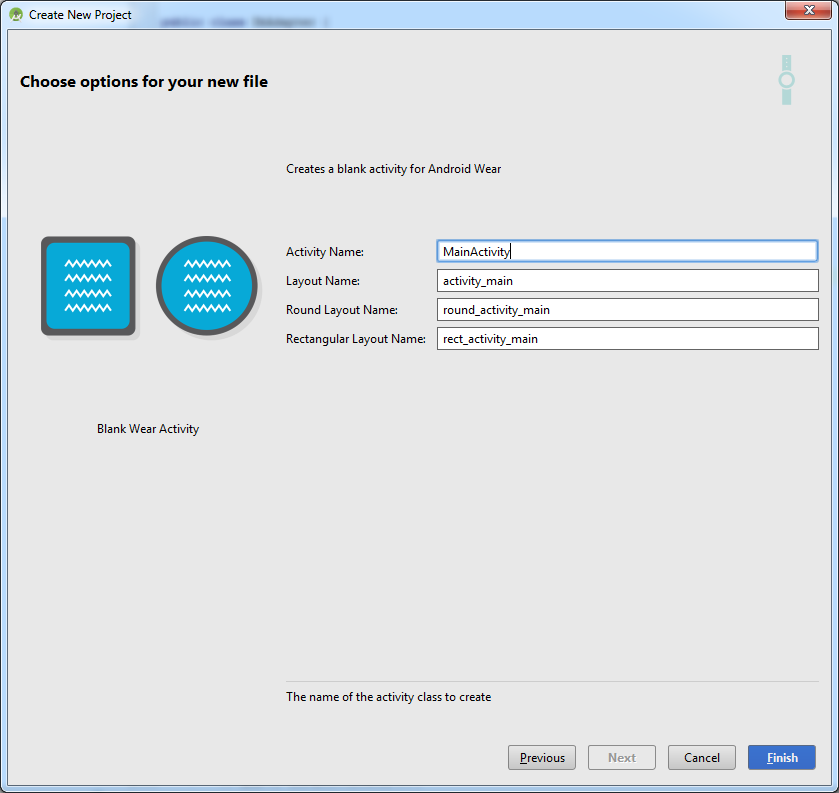
В итоге получим хорошую заготовку для обоих устройств, с пустыми активностями:
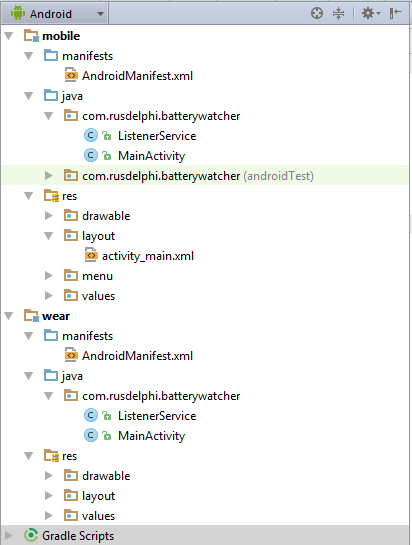
ListenerService сам не появится, ниже расскажу как его добавить.
Чтобы связать наши устройства, был придуман хитрый слой. Приложения могут обмениваться сообщениями через этот слой. Отправка сообщений должна проходить в отдельном потоке. Очень подробно реализация этой задачи описана здесь.
Вы должны подключиться к GoogleApiClient, потом отправить в отдельном потоке сообщение. В примерах это описано подробно, но я решил вынести всю работу с сообщениями в отдельный сервис и получилось довольно компактно.
Вот наш ListenerService, он одинаков для обоих частей проекта.
package com.rusdelphi.batterywatcher;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.support.v4.content.LocalBroadcastManager;
import android.util.Log;
import com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult;
import com.google.android.gms.common.api.GoogleApiClient;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.MessageApi;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.MessageEvent;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.Node;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.NodeApi;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.Wearable;
import com.google.android.gms.wearable.WearableListenerService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Created by User on 04.01.2015.
*/
public class ListenerService extends WearableListenerService {
private SharedPreferences prefs;
private boolean mIsAlarmOn;
GoogleApiClient googleClient;
public static final String ACTION_SM = "com.rusdelphi.batterywatcher.action.SM";
public static final String ACTION_SM_PARAM = "com.rusdelphi.batterywatcher.action.SM.PARAM";
private static final String WEAR_MESSAGE_PATH = "batterywatcher_message_path";
public ListenerService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
googleClient = new GoogleApiClient.Builder(this)
.addApi(Wearable.API)
.build();
googleClient.connect();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
if (null != googleClient && googleClient.isConnected()) {
googleClient.disconnect();
}
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
if (intent != null) {
final String action = intent.getAction();
if (ACTION_SM.equals(action)) {
final String param1 = intent.getStringExtra(ACTION_SM_PARAM);
if (googleClient.isConnected()) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
NodeApi.GetConnectedNodesResult nodes = Wearable.NodeApi.getConnectedNodes(googleClient).await();
for (Node node : nodes.getNodes()) {
MessageApi.SendMessageResult result = Wearable.MessageApi.sendMessage(googleClient, node.getId(), WEAR_MESSAGE_PATH, param1.getBytes()).await();
if (result.getStatus().isSuccess()) {
Log.d("main", "Message: {" + param1 + "} sent to: " + node.getDisplayName());
} else {
// Log an error
Log.d("main", "ERROR: failed to send Message");
}
}
}
}).start();
}
if (!googleClient.isConnected()) new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ConnectionResult connectionResult = googleClient.blockingConnect(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
NodeApi.GetConnectedNodesResult nodes = Wearable.NodeApi.getConnectedNodes(googleClient).await();
for (Node node : nodes.getNodes()) {
MessageApi.SendMessageResult result = Wearable.MessageApi.sendMessage(googleClient, node.getId(), WEAR_MESSAGE_PATH, param1.getBytes()).await();
if (result.getStatus().isSuccess()) {
Log.d("main", "Message: {" + param1 + "} sent to: " + node.getDisplayName());
} else {
// Log an error
Log.d("main", "ERROR: failed to send Message");
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(MessageEvent messageEvent) {
if (messageEvent.getPath().equals(WEAR_MESSAGE_PATH)) {
final String message = new String(messageEvent.getData());
Intent messageIntent = new Intent();
messageIntent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
messageIntent.putExtra("message", message);
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).sendBroadcast(messageIntent);
} else {
super.onMessageReceived(messageEvent);
}
}
}
В оба манифеста нужно его добавить:
<service android:name=".ListenerService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.android.gms.wearable.BIND_LISTENER" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
Во время создания сервиса, мы собираем GoogleApiClient и подключаемся к слою данных.
Событие onMessageReceived вызывается при получении сообщения. У полученного события (MessageEvent) мы смотрим папку назначения (getPath()). Если это наша папка, получаем данные (messageEvent.getData()). Далее эти данные можно сохранить в настройки, базу данных. В общем, использовать как будет нужно. А мы с помощью LocalBroadcastManager отправим их в нашу основную программу (MainActivity). Но для этого локальный приёмник в ней нужно зарегистрировать. Мы это будем делать при старте, а разрегистрировать будем при выходе.
Для отправки сообщения другому устройству мы будем запускать сервис с нужными данными.
В сервисе может быть уже подключен GoogleApiClient, а может и не быть. Если он ещё не подключен, то нужно запустить blockingConnect, иными словами заставить его подключиться напрямую, блокируя соединение. Делать все это нужно в отдельном потоке, т.к. работает это все асинхронно.
Вот код MainActivity для мобильного устройства:
package com.rusdelphi.batterywatcher;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.BatteryManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.content.LocalBroadcastManager;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public static String mWatchLevel = "?", mSmartphoneLevel = "?";
private TextView mWatch;
private TextView mSmartphone;
MessageReceiver messageReceiver = new MessageReceiver();
private BroadcastReceiver mBatteryLevelReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mWatch = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_watch);
mSmartphone = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_smartphone);
IntentFilter batteryLevelFilter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED);
mBatteryLevelReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent i) {
int level = i.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_LEVEL, -1);
int scale = i.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SCALE, -1);
mSmartphoneLevel = new java.text.DecimalFormat("0.0")
.format((((float) level / (float) scale) * 100.0f)) + "%";
sendMessage(MainActivity.this, mSmartphoneLevel);
updateUI();
}
};
registerReceiver(mBatteryLevelReceiver, batteryLevelFilter);
IntentFilter messageFilter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).registerReceiver(messageReceiver, messageFilter);
}
public static void sendMessage(Context context, String param1) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, ListenerService.class);
intent.setAction(ListenerService.ACTION_SM);
intent.putExtra(ListenerService.ACTION_SM_PARAM, param1);
context.startService(intent);
}
public void updateUI() {
mWatch.setText(mWatchLevel);
mSmartphone.setText(mSmartphoneLevel);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
updateUI();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).unregisterReceiver(messageReceiver);
if (mBatteryLevelReceiver!=null) {
unregisterReceiver(mBatteryLevelReceiver);
mBatteryLevelReceiver=null;
}
super.onDestroy();
}
public class MessageReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String message = intent.getStringExtra("message");
mWatchLevel = message;
updateUI();
}
}
}
Тут мы при старте создаем приемник, получающий сообщения о батареи устройства. Как только получили сообщение (onReceive), отправляем его сообщением в слой данных (sendMessage) и обновляем значения переменных (updateUI). Далее регистрируем локальный приемник (MessageReceiver), он при приеме также обновит экран приложения (updateUI).
Вот код MainActivity для wear-устройства, т.е. для часов:
package com.rusdelphi.batterywatcher;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.BatteryManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.content.LocalBroadcastManager;
import android.support.wearable.view.WatchViewStub;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public static String mWatchLevel = "?", mSmartphoneLevel = "?";
private TextView mWatch;
private TextView mSmartphone;
MessageReceiver messageReceiver = new MessageReceiver();
private BroadcastReceiver mBatteryLevelReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final WatchViewStub stub = (WatchViewStub) findViewById(R.id.watch_view_stub);
stub.setOnLayoutInflatedListener(new WatchViewStub.OnLayoutInflatedListener() {
@Override
public void onLayoutInflated(WatchViewStub stub) {
mWatch = (TextView) stub.findViewById(R.id.tv_watch);
mSmartphone = (TextView) stub.findViewById(R.id.tv_smartphone);
updateUI();
}
});
IntentFilter batteryLevelFilter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED);
mBatteryLevelReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent i) {
int level = i.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_LEVEL, -1);
int scale = i.getIntExtra(BatteryManager.EXTRA_SCALE, -1);
mWatchLevel = new java.text.DecimalFormat("0.0")
.format((((float) level / (float) scale) * 100.0f)) + "%";
sendMessage(MainActivity.this, mWatchLevel);
updateUI();
}
};
registerReceiver(mBatteryLevelReceiver, batteryLevelFilter);
IntentFilter messageFilter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).registerReceiver(messageReceiver, messageFilter);
}
public void updateUI() {
if (mWatch != null)
mWatch.setText(mWatchLevel);
if (mSmartphone != null)
mSmartphone.setText(mSmartphoneLevel);
}
public static void sendMessage(Context context, String param1) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context, ListenerService.class);
intent.setAction(ListenerService.ACTION_SM);
intent.putExtra(ListenerService.ACTION_SM_PARAM, param1);
context.startService(intent);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this).unregisterReceiver(messageReceiver);
if (mBatteryLevelReceiver != null) {
unregisterReceiver(mBatteryLevelReceiver);
mBatteryLevelReceiver = null;
}
super.onDestroy();
}
public class MessageReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String message = intent.getStringExtra("message");
mSmartphoneLevel = message;
updateUI();
}
}
}
Он, в принципе, похож на старшего брата, но есть отличия в постройке разметки, т.к. устройства могут быть с квадратными и круглыми экранами. Компонент WatchViewStub дает нам возможность упростить выбор разметки, для этого нужно просто спроектировать 2 файла rect_activity_main.xml и round_activity_main.xml.
Вот код первого:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
tools:deviceIds="wear_square">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:src="@drawable/watch" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv_watch"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
style="@style/TextAppearance.Wearable.Large" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:src="@drawable/smartphone" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv_smartphone"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
style="@style/TextAppearance.Wearable.Large" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
Вот второго:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
tools:deviceIds="wear_round">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true">
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:src="@drawable/watch" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv_watch"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
style="@style/TextAppearance.Wearable.Large" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:src="@drawable/smartphone" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv_smartphone"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
style="@style/TextAppearance.Wearable.Large" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
Здесь при создании разметки мы получаем два компонента TextView и обновляем их содержание (updateUI). Остальной код работает так же как и в мобильной версии. Запускаем приложение, получаем текущий уровень батареи, отправляем его соседнему устройству и слушаем его сообщения. Как что-то изменилось -> обновляем показания.
При публикации приложения в гугл маркете у обоих модулей должен быть одинакова версия (versionCode) кода и одинаковое имя пакета. По умолчанию Android Studio эту работу за нас сделает. Когда соберем apk файл для мобильного устройства, внутри него будет находиться apk для wear. Эту работу можно сделать и в Eclipse. В общем, кому как проще. При установке приложения из маркета на мобильное устройство придет толстый apk, который сам установит apk для wear устройства.
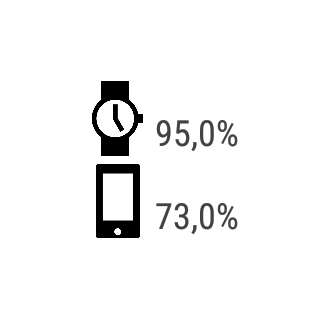
Скриншоты с устройств:

Автор: petrovichtim





![Мой опыт собеседования в Google [оффер на L5] Мой опыт собеседования в Google [оффер на L5]](https://www.pvsm.ru/wp-content/plugins/contextual-related-posts/timthumb/timthumb.php?src=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.pvsm.ru%2Fimages%2F2023%2F12%2F05%2Fmoi-opyt-sobesedovaniya-v-Google-offer-na-L5.jpg&w=100&h=100&zc=1&q=75)